Figure 6.
Caf1 Destabilizes mRNAs with Low Codon Optimality by Accelerating Deadenylation Rate
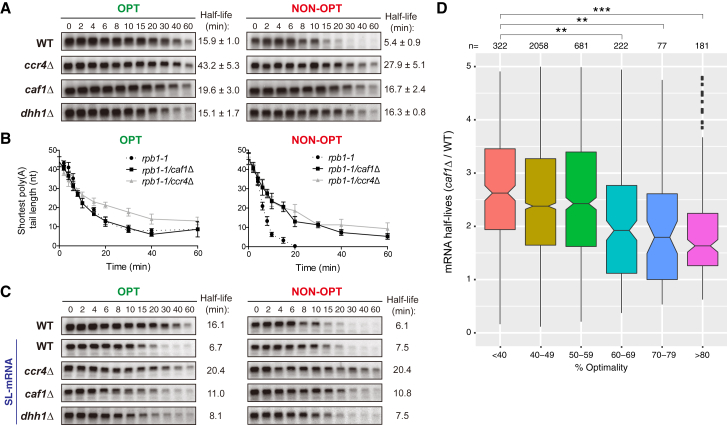
(A) Northern blots of the OPT and NON-OPT reporters following GAL1 transcriptional shut-off experiments in WT, ccr4Δ, caf1Δ, and dhh1Δ yeast. mRNA half-lives are represented as mean ± standard deviation for experiments performed with four (dhh1Δ, ccr4Δ) or five (WT, caf1Δ) replicates.
(B) Plots showing the deadenylation rate of the OPT and NON-OPT reporters in rpb1-1, rpb1-1/ccr4Δ, or rpb1-1/caf1Δ yeast determined from transcriptional pulse-chase experiments (see Figure S7). Data points are represented as mean ± standard deviations for experiments performed in triplicate.
(C) Northern blots of OPT and NON-OPT reporters in WT yeast and OPT and NON-OPT reporters containing a stem loop (SL) in the 5′ UTR (SL-mRNA) in WT, ccr4Δ, caf1Δ, or dhh1Δ yeast after GAL1 transcriptional shut-off experiments.
(D) Plot of S. cerevisiae mRNA half-lives in caf1Δ cells relative to WT cells binned according to codon optimality. ∗∗: 10−2 > padj > 10−3; ∗∗∗padj < 10−3.