Figure 3.
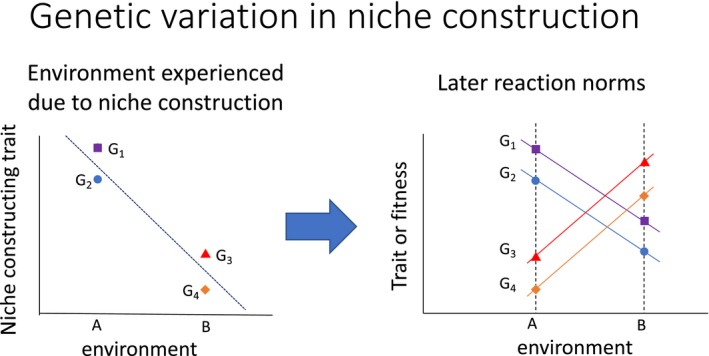
How genetic variation in niche construction may produce G × E. Individuals’ experience in particular environments, which is a function of their niche‐constructing traits (left) may influence their reaction norms when measured at a later time (right) resulting in G × E. Left: Genotypes 1 and 2 have high levels of a niche‐constructing behavior (e.g., sociability) and therefore occur in environment a (e.g., large group size), while genotypes 3 and 4 have low levels of the niche‐constructing behavior and therefore occur in environment b. Due to experiences in environments a or b, genotypes develop differences in their reaction norms across environments a and b (right), resulting in G × E. In this example, genotypes have higher trait (or fitness) values in the environment (a or b) they previously experienced, relative to the alternate environment, but other patterns are possible
