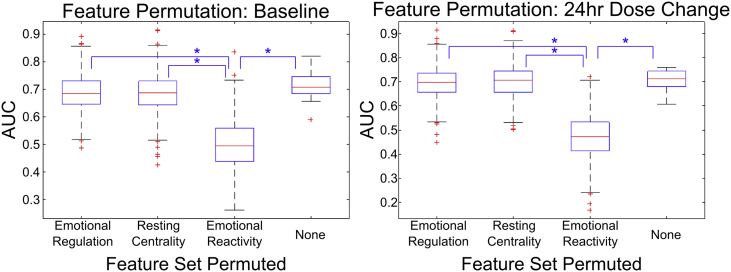
Fig. 5.
The impact to the classification accuracy of the fMRI predictor algorithm when certain feature map sets are permuted between subjects is shown via interquartile boxplots. The first three columns represent the result of shuffling the features of a given fMRI metric map between subjects, while the last column represents the accuracy when no features are permuted. Note that the largest drop in accuracy occurs when the emotional reactivity features are permuted, indicating the utility of using a task to probe specific features of neural activity. Statistical significance was determined via two-sample t-tests. All the pairs marked by asterisks have a p-value bound below 10−35.