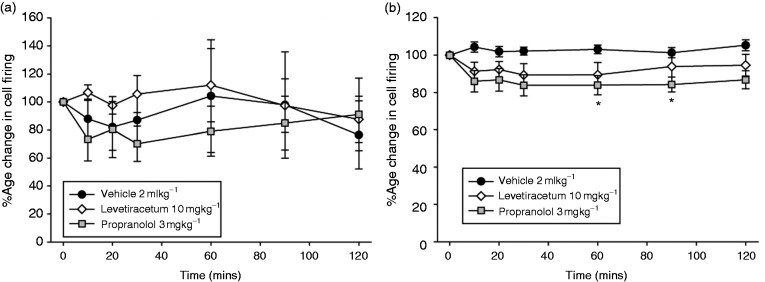
Figure 6.
Effects of propranolol and levetiracetam on nociceptive trigeminovascular activation. Time course changes in (a) ongoing spontaneous trigeminal neuronal firing and (b) the average response of intracranial dural-evoked Aδ-fiber trigeminal neurons to intravenous administration of saline, propranolol (3 mg/kg) and levetiracetam (10 mg/kg). Levetiracetam had no effect on either ongoing spontaneous or intracranial dural-evoked Aδ-fiber trigeminal neuronal firing. Propranolol had no effect on ongoing spontaneous trigeminal neuronal firing, but caused significant inhibition of intracranial dural-evoked Aδ-fiber trigeminal firing after 75–90 min. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 compared with an average of the four baselines, using Student’s paired t test.