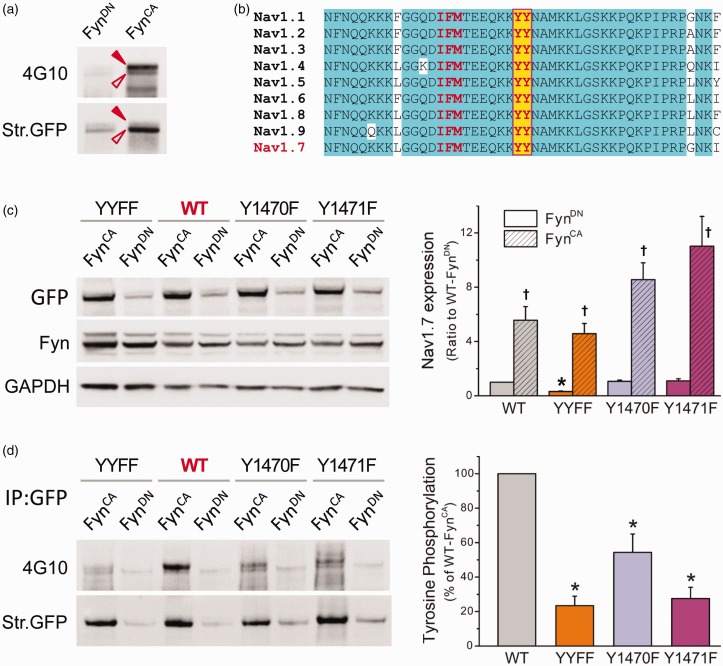
Figure 3.
Nav1.7 is subject to FynCA-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. (a) FynCA or FynDN was transfected in HEK-Nav1.7st cells, and Nav1.7 channels were precipitated from cell lysate using antisodium channel antibody (PanNav). Tyrosine phosphorylation level was examined by antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10 (upper panel), the blot was then stripped and reprobed with PanNav antibody to reveal total Nav1.7 channels pulled down by PanNav (bottom panel). Two phosphotyrosine bands were detected, probably due to different glycosylation levels. The pull-down sample from cells expressing FynCA produced strong phosphotyrosine signal, demonstrating the contribution of Fyn to tyrosine phosphorylation of Nav1.7 channels. (b) The sequence alignment of the L3 of Nav1.7, which is highly conserved among human VGSCs. The tyrosine residues (highlighted with yellow color) are six residues away from the IFM inactivation motif. (c) Total protein expression of WT and mutant channels when cotransfected with FynCA or FynDN. The WT, Y1470F, and Y1471F channels exhibited similar total protein expressions when cotransfected with FynDN, while the expression of the YYFF double mutant was reduced. FynCA caused a significant increase in protein expression of all four constructs. Data are presented as means ± SE, *p < 0.05 versus total expression of WT/FynDN, †p < 0.05 versus corresponding channels cotransfected with FynDN, one-way ANOVA test. (d) The tyrosine phosphorylation levels of WT and mutant channels. The WT or mutant constructs were cotransfected with FynCA or FynDN in HEK 293 cells, and Nav1.7 channels were precipitated from cell lysate using anti-GFP antibody. Tyrosine phosphorylation level was examined by antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10 (upper panel), the blot was then stripped and reprobed with anti-GFP antibody to reveal total WT or mutant Nav1.7 channels immunoprecipitated by anti-GFP antibody (bottom panel). Substitution of either Y1470 or Y1471 or both dramatically reduced the phosphotyrosine levels of mutant channels, suggesting that both tyrosine residues are involved in Fyn-induced phosphorylation of Nav1.7 channels. The right panel is the histogram of FynCA-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of WT and mutant channels presented as the percentages of the phosphotyrosine level of WT channels. Data are presented as mean ± SE, *p < 0.05 versus WT/FynCA by one-way ANOVA test. WT: wild-type; YYFF: Nav1.7rG-Y1470F/Y1471F; GFP: Green Fluorescent Protein; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase.