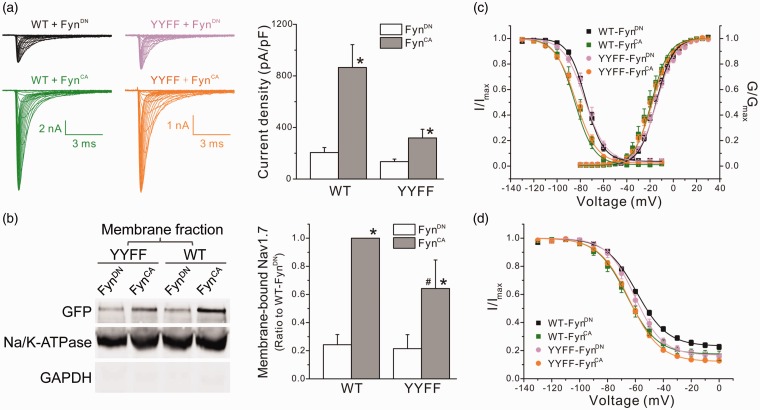
Figure 6.
FynCA modulated the biophysical properties of Nav1.7 in ND7/23 cells through mechanisms unrelated to phosphorylation of Y1470 and Y1471. (a) The left panels shows the representative WT or YYFF mutant currents recorded from ND7/23 cells cotransfected with FynCA or FynDN. Cells expressing WT channels generated relative larger sodium currents when compared with cells expressing mutant channels. The right panel is the histogram of the mean current densities. FynCA increased current densities of both WT and YYFF mutant channels. Data are presented as means ± SE, *p < 0.05 versus corresponding FynDN control by Mann–Whitney test. (b) The left panel shows the representative Western blot image of membrane expression of WT and YYFF mutant channels cotransfected with FynCA or FynDN in ND7/23 cells. The right panel is the histogram of mean surface expressions of WT and YYFF channels normalized by the membrane expression level of WT/FynCA. Data are obtained from six experiments and presented as mean ± SE, *p < 0.05 WT/FynCA versus WT/FynDN or YYFF/FynCA versus YYFF/FynDN; #p < 0.05, YYFF/FynCA versus WT/FynCA, by one-way ANOVA test. (c) The activation and steady-state fast inactivation curves of WT and mutant channels cotransfected with FynCA or FynDN. FynCA shifted both activation and fast inactivation curves of WT channels to the hyperpolarizing direction in ND7/23 cells, which was remained in mutant channels. Data are presented as means ± SE. (d) The steady-state slow inactivation of WT and YYFF mutant channels. FynCA shifted the slow inactivation curve of both channels to the hyperpolarizing direction and reduced the percentage of channels that are resistant to slow inactivation (Rresist). Data are presented as means ± SE. WT: wild type; YYFF: Nav1.7rG-Y1470F/Y1471F; GFP: Green Fluorescent Protein; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase.