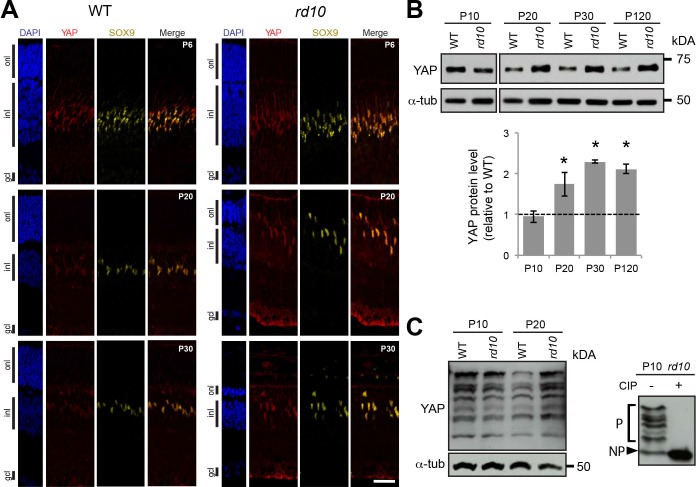
Figure 6.
YAP expression during retinal degeneration. (A) Coimmunostaining with anti-YAP (red) and anti-SOX9 (yellow) antibodies on retinal sections of WT and rd10 mice at different stages from P6 to P30. Nuclei are DAPI counterstained (blue). (B) Representative western blots of retinal protein extracts from WT and rd10 mice at different stages from P10 to P120, probed with anti-YAP antibody or anti-α-tubulin (α-tub) as a loading control. Histogram representation of YAP quantification from western blot signals normalized to α-tubulin and relative to WT at each stage (dashed line). Mean values ± SEM from four independent western blot experiments are shown. Asterisk indicates P value ≤ 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). (C) Representative western blots of retinal protein extracts from WT and rd10 mice at P10 and P20 using Phos-tag gel and probed with anti-YAP antibody or anti-α-tubulin (α-tub; left panel). The shifted bands correspond to YAP phosphorylated isoforms since they are lost following Calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (+CIP) treatment on rd10 P10 lysate (right panel). P, phosphorylated forms of YAP; NP, nonphosphorylated form of YAP; onl, outer nuclear layer; gcl, ganglion cell layer. Scale bars: 20 μm.