Table 3.
Spontaneous mutations in different EV-A71 subgenotypes (BrCr, B1-B5, C1-C5).
| Mutant Strains of EV-A71 | Position of Amino Acid(s) on the EV-A71 Genomes of Mutants | Significance of the Mutations in the EV-A71 Genome | References |
|---|---|---|---|
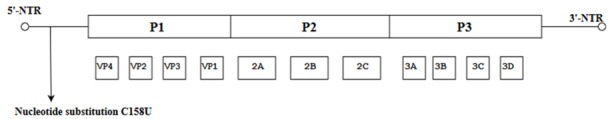
| Analysis of EV-A71 subgenotype C4 showed changes in the 5′-NTR and the VP1. |
|
When the nucleotide cytosine was substituted with uridine at position 158, the conformation of the RNA secondary structure of stem loop II in the 5′-NTR changed, leading to a decrease in viral translation and virulence in mice. | [38] |
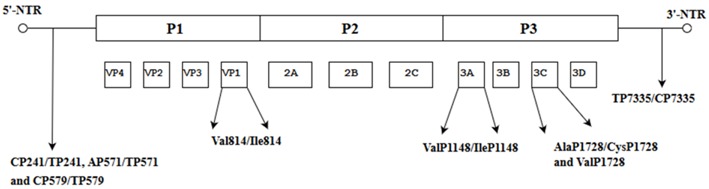
| Nucleotide and amino acid changes in neuro-virulent strains of EV-A71 subgenotype C4a. |
|
These amino acids are potential molecular determinants of virulence. Variations in the secondary structure of the 5′-NTR at three positions (CP241/TP241, AP571/TP571 and CP579/TP579) and one position in the 3′-NTR(TP7335/CP7335) might confer fatality. | [39] |
| Comparisons of EV-A71 across different genotypes (BrCr, B1-B5 and C1-C5) |
|
These amino acid residues might be associated with the EV-A71 virulentphenotype. | [40] |
| Changes in VP1 sequences of EV-A71 subgenotype C4 causing severe HFMD |
|
E145Q/G interacts with residues of the PSGL-1 N-terminus and acts as a molecular switch to modulate binding to the cell receptor by controlling the exposure of the amino acid (VP1-244K) on the VP1 surface. | [41,42] |
| Analysis of EV-A71 subgenotype C4 showed changes in the 5′-NTR and the VP1 |
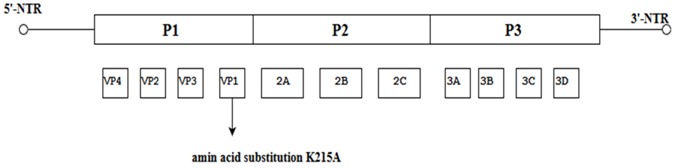
|
K215A located at the VP1 GH loop increased the thermal stability of the virus. | [44] |
| Roles of K244E and H37R were investigated by reverse engineering in the EV71-B2 isolate, MS/7423/87 |
|
It was postulated that H37E and K244E interactions were important for replication in primate cells but K244E alone was able to confer the ability of the virus to replicate alone in a murine model | [45] |
| Role of K216→R, G145→E and K129→I in the mouse-adapted strain of EV-A71 26M/AUS/4/99 |
|
G145→E mutation was solely responsible for an increase in virulence in mice whilst K129→I led to an improved growth of the strain in vitro but did not lead to increased virulence in mice | [48] |
| Analysis of the genomes of six EV-A71 strains of subgenotype C4a identified the only change of amino acid Asn 1617 in the 3C gene |
|
This specific amino acid led to conformational change at the active centre of the 3C proteinase (3Cpro) and this could be a potential molecular determinant for the EV-A71. | [49] |
Analysis of different EV-A71 strains showing the position of the spontaneous mutations present in the genomes of EV-A71 and their significant impact on virulence.
