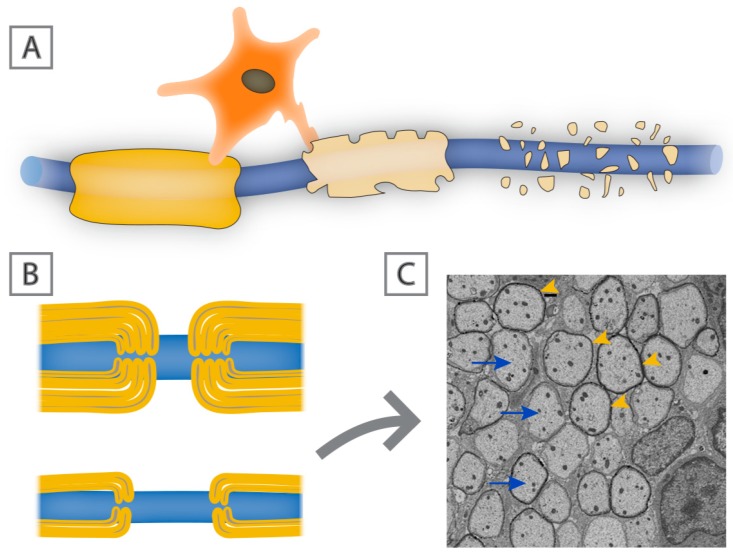
Figure 3.
Demyelination vs. remyelination. Schematic of a myelinated axon (A), in which there is oligodendrocyte dysfunction and subsequent loss of myelin sheaths. Remyelinated axons ((B); lower panel) are characterized by thin myelin sheaths. (C) Electron micrograph of axons (arrows) in the dorsal white matter of the spinal cord in an adult rat showing thin myelin sheaths (arrowheads) following lysolecithin-induced demyelination.