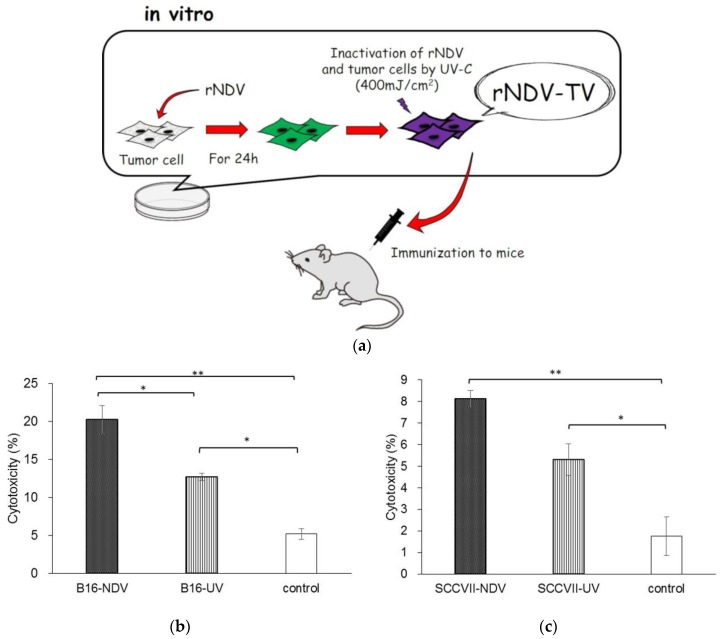
Figure 1.
Newcastle disease virus (NDV)-infected tumor vaccines (NDV-TV) model and induction of antitumor response by rNDV-TV. (a) The schematic of NDV-TV model was shown. The tumor cells were infected with rNDV in vitro, irradiated by ultraviolet for inactivation of rNDV and tumor cells. Then rNDV-TV was administered to mice as immunogen. rNDV-TV (n = 3), UV-TV (ultraviolet irradiated tumor vaccine) (n = 3), or each medium (n = 2) were administered to mice and splenic mononuclear cells (SMCs) were co-cultured with UV-irradiated tumor cells for 5 days. After cytotoxic T cell (CTL) induction, SMCs were harvested and co-cultured with target tumor cells for 24 h. The cytotoxicity was measured using quantifying lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the supernatant (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). rNDV-TV and UV-TV were prepared using (b) B16 and (c) SCC VII. Medium was administered to the control mice.