Table 1.
Non-classical α-conotoxins and their pharmacology.
| Superfamily | Sequence, Cysteine Framework and Connectivity | Pharmacology |
|---|---|---|
| A superfamily | ||
| AuIB |
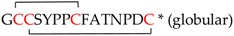
|
non-competitive inhibitor of the α3β4 [99] |
| AuIB |
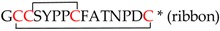
|
10-fold more potent in rat parasympathetic ganglions than the globular isomer |
| AusIA |

|
Defines a new 5/5 subclass. Both globular and ribbon isomers are equipotent at α7 [101] |
| ImII |

|
Lacks conserved proline in loop 1. Allosteric inhibitor of the α7 |
| LtIA |

|
Ala-Xaa-Ala motif substitutes the conserved Ser-Xaa-Ser motif. Competitive blocker with a shallow binding pocket. |
| Lp1.1 |

|
Ala-Xaa-Ala motif substitutes the conserved Ser-Xaa-Ser motif |
| MrIC |
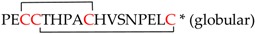
|
State dependent activator of the α7 |
| Eu1.6 |
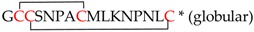
|
α-conotoxin inhibiting Cav 2.2 [107] |
| S superfamily | ||
| RVIIIA | KCNFDKCKGTGVYNCG(Gla)SCSC(Gla)GLHSCRCTYNIGSMKSGCACICTYY | Atypical cysteine framework. Cysteine connectivity unknown. No C-terminal amidation. Two γ-carboxyglutamates. Broad selectivity: α7, α6/α3β2β3, α3β2 and to a smaller extent the α3β4 and α4β2 [9] |
| GVIIIA | GCTRTCGGOKCTGTCTCTNSSKCGCRYNVHPSG(BTr)GCGCACS * | Cysteine connectivity unknown. C-terminal amidation and bromo-tyrosine present as post-translational modification. Selective α9α10 inhibitor |
| D superfamily | ||
| VxXXA | DVQDCQVSTOGSKWGRCCLNRVCGPMCCPASHCYCVYHRGRGHGCSC | Dimeric peptides. Allosteric inhibitors of the α7, α3β2 and α4β2. |
| VxXXB | DD(Gla)S(Gla)CIINTRDSPWGRCCRTRMCGSMCCPRNGCTCVYHWRRGHGCSCPG | |
| VxXXC | DLRQCTRNAPGSTWGRCCLNPMCGNFCCPRSGCTCAYNWRRGIYCSC | |
| GeXXA |

|
Dimeric peptide. Allosteric inhibitors of the α9α10. ‘Lid covering’ binding mode. |
| B3 superfamily | ||
| VxXXIVA |

|
Potency dependent on disulfide connectivity—[1,2] 1.2 µM > [1,3] 3.9 µM > [1,4] > 30 µM, suggesting that the novel cysteine framework is important for its mode of action [26] |
| O1 superfamily | ||
| GeXIVA |

|
|
| T superfamily | ||
| TxVC |

|
α4β2 inhibitor. Members of this superfamily typically target Cav channels. |
| J superfamily | ||
| pl14a |

|
Targets Kv1.6 and α3β4 |
| M superfamily | ||
| CnIIIC |

|
Targets Nav 1.2, 1.4 together with α3β2 |
(*) C-terminal amidation, (Gla) Gamma carboxylic glutamic acid, (BTr) bromotyrosine, (†) forms inter-chain disulfide bonds (Z) Pyroglutamic acid.
