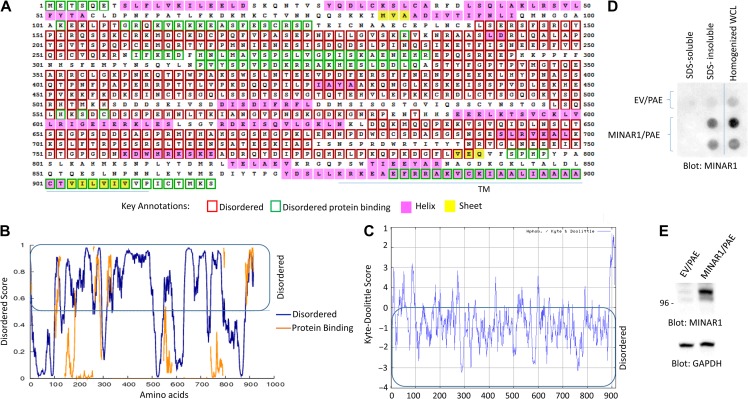
Figure 1.
Identification of MINAR1 as an IDP. (A) The amino acid sequence of human MINAR1. Amino acids boxed in the red correspond to disordered segments of MINAR1. The data were generated using online DISOPRED3 (Disorder Prediction) program. (B) The graph is the representation of the data shown in A. (C) The Kyte–Doolittle hydrophobicity score of MINAR1. The graph was generated using online program http://web.expasy.org/protscale/. (D) PAE cells ectopically expressing empty vector (EV) or MINAR1 were lysed with lysis buffer containing Triton X-100. Whole-cell lysates (WCL) were centrifuged and Triton X-100 soluble fraction was separated from the insoluble fraction. The remaining insoluble fraction was further solubilized with 1% SDS. Both fractions were then blotted on cellulose acetate filter via a dot blot apparatus. The same cell groups were also homogenized in PBS plus 1% SDS and similarly blotted on cellulose acetate filter. The cellulose acetate filter was blotted for the presence of MINAR1 using anti-MINAR1 antibody (the MINAR1/PAE cell lysate group loaded in duplicate). (E) Western blot of the cell lysates from EV/PAE and MINAR1/PAE. Data in D and E are representative of at least three independent experiments.