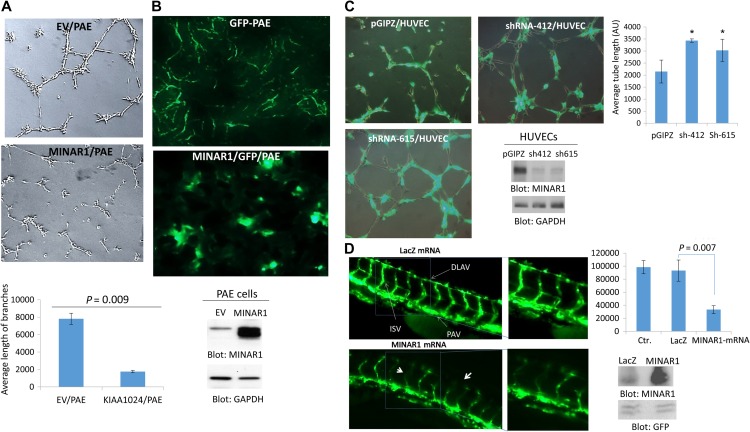
Figure 3.
MINAR1 inhibits in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis. (A) PAE cells ectopically expressing empty vector (EV) or MINAR1 were subjected to in vitro angiogenesis assay and pictures were taken after 24 h. Pictures were taken and three randomly selected pictures from each group were selected and quantified using Image J program. (B) GPP-PAE cells expressing empty vector (EV) or MINAR1 were subjected to in vivo matrigel assay. Cells were mixed with growth factor-reduced matrigel and sub-dermally injected into mouse (three mice/group). After 7 days, the matrigel plugs were removed and were viewed under fluorescent microscope after cryo fixing and processing. The representative pictures are shown (40×). Expression of MINAR1 in PAE cells is shown. (C) HUVECs were transduced with an empty vector, pGIPZ, or two different MINAR1 shRNA. After 48 h, cells were subjected to in vitro angiogenesis assay. Cells were viewed under a fluorescent microscope and pictures were taken. Quantification of capillary tube formation was made by Image J program. Knockdown of MINAR1 is also shown. (D) Fli-eGFP transgenic fish embryos were injected with MINAR1 or LacZ mRNA at the 1-cell stage or 2-cell stage. The embryos were examined at 50 h post-fertilization (50 hpf) and representative immunofluorescence images are shown. Quantification of intersegmental vessels (ISV) and the dorsal lateral anastomosing vessel (DLAV) of 10 fish per group by ImageJ are shown in bar graph. Error bars represent SD. P = 0.007 for 10 ng MINAR1 mRNA compared with LacZ control. Western blot analysis of MINAR1 expression from tissue lysates of microinjected fish is performed with anti-MINAR1 antibody and protein loading control GFP.