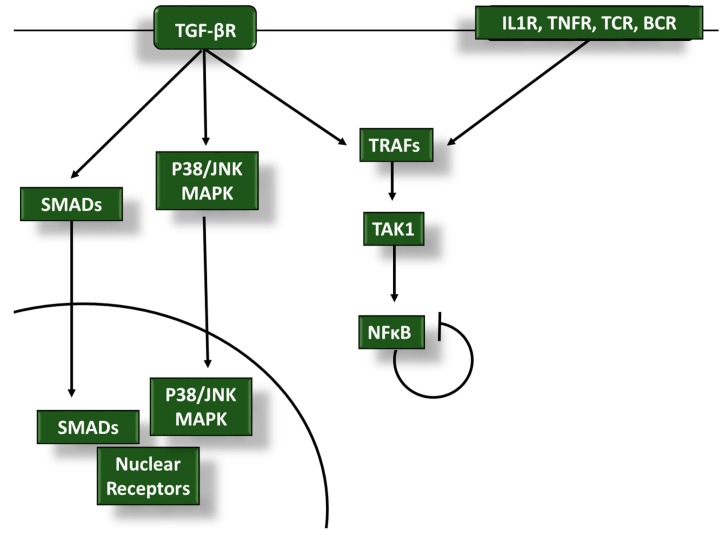
Figure 2.
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) dampens anti-tumor proinflammatory signaling in infiltrating leukocytes through TGF-β activated kinase 1 (TAK1), nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) modulation: tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor (TRAF) and TAK1 activity is regulated by the anti-inflammatory TGF-β receptor (TGF-βR) and proinflammatory interleukin 1 receptor (IL-1R), TNFRs, T cell receptors (TCRs), and B cell receptors (BCRs). TGF-β signaling interferes with TRAF and TAK1 activation to alter NFκB signaling in tumor-associated leukocytes to blunt immune responses during cancer progression. TGF-β modulation of the p38/JNK MAPK pathways and SMAD activity also play a role in inhibiting proinflammatory signals.