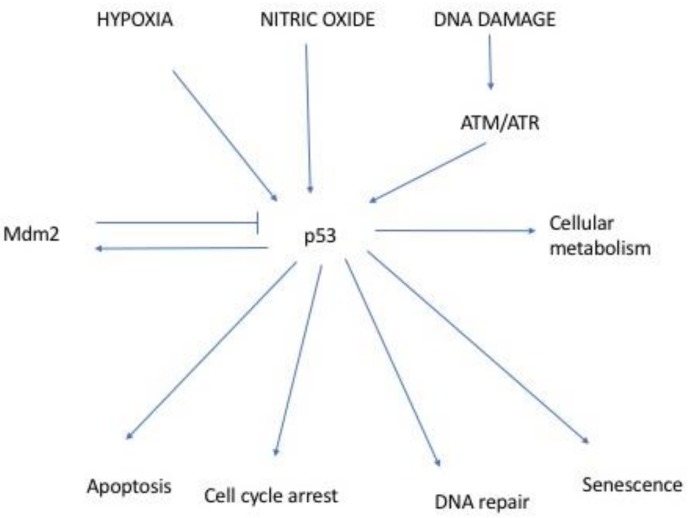
Figure 1.
Basic functions of p53. p53 levels are tightly controlled and in unperturbed cells MDM2 is its main regulator via induction of p53 degradation. There is a negative feedback loop between the two proteins. p53 itself induces MDM2 transcription, hence as p53 levels increase, more MDM2 is produced, which in turn down regulates p53 levels. In the presence of DNA damage and other stresses, p53 degradation stops and its levels increase. Elevated levels of stabilized p53 induce transcription of proteins involved in different types of responses, particularly cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Modified schematic diagram [8].