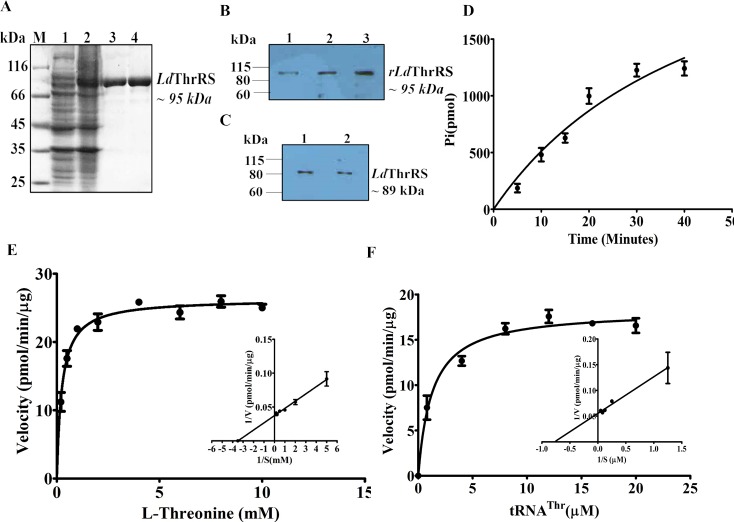
Fig 1. Expression, purification, western blot and enzymatic activity of LdThrRS.
(A) Induction and purification of recombinant LdThrRS (rLdThrRS) by Ni2+-NTA affinity chromatography. M, molecular weight marker; Lane 1, uninduced cell lysate; Lane 2, induced cell lysate; Lane 3 and 4, eluted fractions with 300 mM imidazole showing purified rLdThrRS. (B) Western blot analysis of rLdThrRS with anti-LdThrRS antibody (1:1000), Lane 1, 0.5 μg of rLdThrRS; Lane 2, 1 μg of rLdThrRS; Lane 3, 2 μg of rLdThrRS. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the cell lysate of 30 μg Leishmania with the anti-LdThrRS antibody (1:1000), Lane 1: promastigote; Lane 2: amastigote. (D) Time-dependent aminoacylation assay of rLdThrRS. The aminoacylation reactions were performed with L-threonine and tRNAThr as the substrates. The result shows an average of three different experiments performed in duplicate ± SD. (E) and (F) The aminoacylation kinetics catalyzed by rLdThrRS as a function of L-threonine (E) and tRNAThr (F) concentration. The kinetic parameters were calculated by a Michaelis-Menten algorithm within GraphPad Prism 5.0 for utilization of L-threonine and tRNAThr by the rLdThrRS enzyme. Results are representative data from three separate experiments and are represented as mean ± S.D.