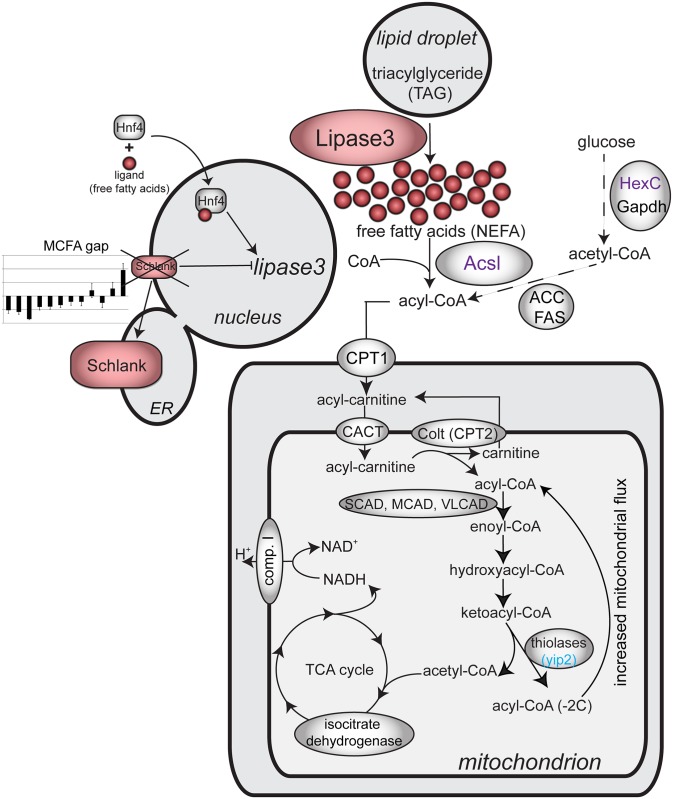
Fig 7. Summary of the role of Schlank in the pathology of Pex19 mutants.
The ceramide synthase Schlank leaves the nuclear membrane compartment in Pex19 mutants as a result of reduced amounts of MCFA, thereby releasing repression of lip3. As a result, increased lipolytic activity of Lip3 leads to release of free NEFAs from fat stores. In a previous study, we identified Hnf4 as a regulator of increased lipolysis in Pex19 mutants: upon fatty acid binding, Hnf4 enters the nucleus and activates target genes, among them lip3, thereby initiating a spiral of lipolysis and further Hnf4 activation by NEFA. Upon coconut oil feeding, the MCFA gap is filled, and Schlank reenters the nuclear membrane compartment and regains its ability to repress lip3, thereby ameliorating the Pex19 phenotype and reducing the free fatty acid load. Transcriptional analysis revealed that the Hnf4 target genes HexC and Acsl are normalized upon coconut oil treatment (purple), while the opposite is true for another Hnf4 target: yip2 is even more highly expressed on the coconut oil diet (blue). ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; Acsl, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain; CACT, carnitine acylcarnitine translocase; Colt, congested-like trachea; CPT, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FAS, fatty acid synthase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HexC, hexokinase C; Hnf4, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4; Lip3, lipase 3; MCAD, medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; MCFA, medium-chain fatty acid; NEFA, nonesterified fatty acid; SCAD, short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; VLCAD, very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; yip2, yippee-interacting protein 2.