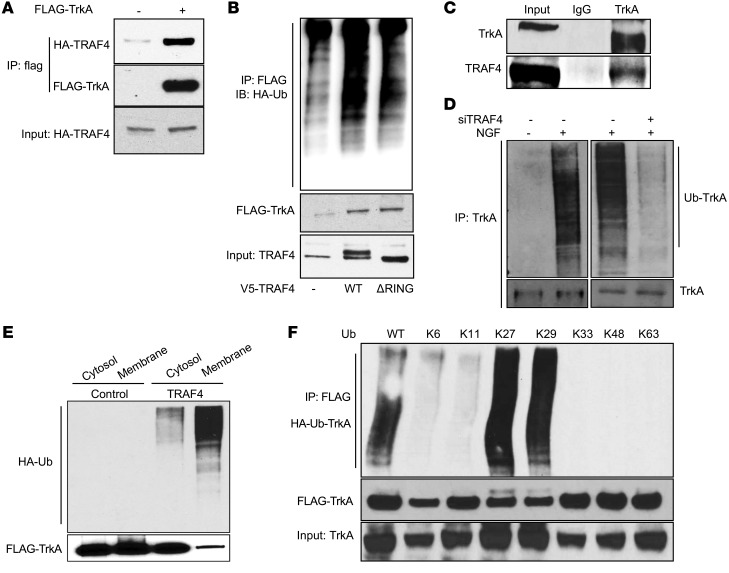
Figure 4. TRAF4 interacted with TrkA and promoted its ubiquitination.
(A) HA-TRAF4 interacted with FLAG-TrkA in transiently transfected 293T cells. Shown is a co-IP experiment using an anti-FLAG antibody for immunoprecipitation. (B) WT TRAF4 but not the RING domain deletion mutant promoted TrkA ubiquitination. 293T cells were cotransfected with constructs as indicated. FLAG-TrkA was immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody, and the ubiquitinated TrkA was visualized by Western blot analysis using an anti-HA antibody. (C) Endogenous TrkA interacted with endogenous TRAF4 in DU145 cells. Shown is a co-IP experiment using a TrkA-specific antibody or IgG control for immunoprecipitation. (D) TRAF4 knockdown abolished NGF-induced TrkA ubiquitination. DU145 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siTRAF4 and HA-ubiquitin. Cells were then treated with 50 ng/ml NGF for 15 minutes before harvest. Ubiquitinated TrkA was detected using an anti-ubiquitin antibody in a Western blot analysis from cell lysates immunoprecipitated with an anti-TrkA antibody. Ub, ubiquitin. (E) TRAF4 overexpression promoted TrkA ubiquitination at the cell membrane. 293T cells were cotransfected with TrkA and HA-Ub in the absence or presence of TRAF4 cotransfection. Cytosolic and membrane fraction were isolated and subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-FLAG antibody, and the ubiquitinated TrkA was visualized by Western blot analysis using an anti-HA antibody. (F) TRAF4-mediated TrkA polyubiquitination through K27- or K29-linked ubiquitin chain. K6–K63 represent the ubiquitin mutant with all lysine mutations except the indicated number of lysine.