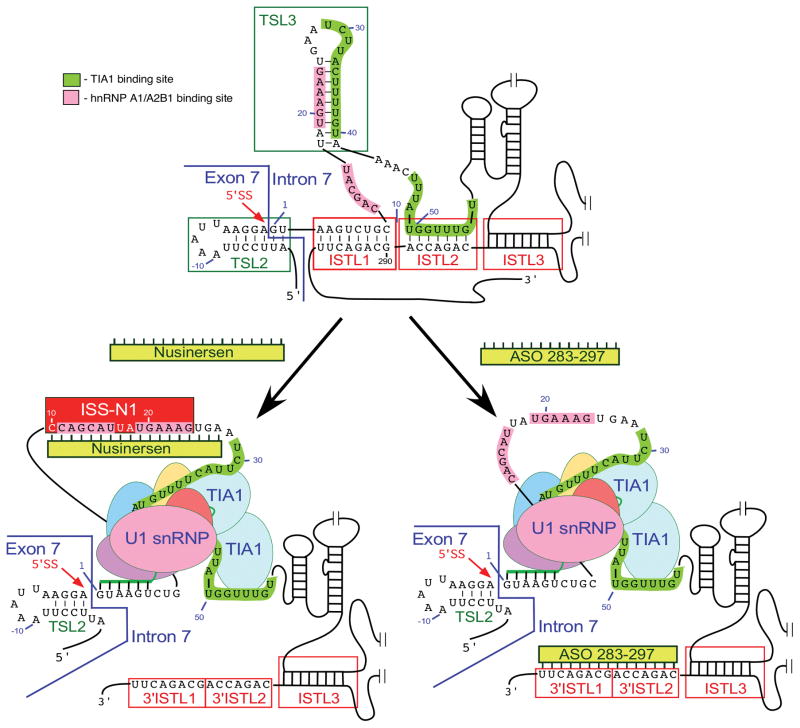
Fig. 5.
ASO-based mechanism of SMN2 exon 7 splicing correction. Only the relevant sequences of exon 7/intron 7 are given. Nucleotide numbering starts from the first position of intron 7. ISS-N1 and the binding sites for TIA1 and hnRNP A1/A2B1 are marked by colored boxes. The 5′ ss of exon 7 is indicated by a red arrow. The annealing positions of U1 snRNA to this 5′ ss are shown. TSL2 and 3 are local RNA secondary structures, while ISTL1, 2 and 3 are the structures formed by long-distance interactions. These structures are boxed. Nusinersen and ASO 283–297 are shown as yellow bars [25, 107]. Their annealing positions within intron 7 are indicated. Targeting of the corresponding intronic sequences by Nusinersen and ASO 283–297 causes massive structural rearrangements, including disruption of TSL3 and ISTL1. As the results TIA1-binding sites become accessible, the recruitment of U1 snRNP to the 5′ ss of exon 7 is increased and, in case of Nusinersen, the binding of hnRNP A1/A2 to ISS-N1 is blocked. Abbreviations are given in Table 2.