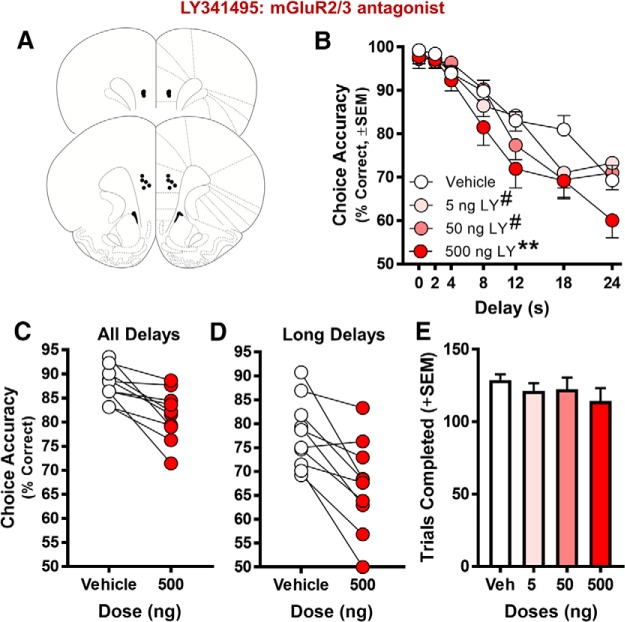
Figure 5.
Effect of micro-infusing LY341495 (mGluR2/3 antagonist) into PrL cortex on performance in the delayed response working memory task. A, Histologically verified placements of injector tips used to micro-infuse the mGluR2/3 antagonist LY341495 into the PrL cortex of young adult rats before testing in the delayed response task (n = 10 young rats). B, Microinfusion of LY341495 significantly reduced choice accuracy relative to vehicle at all doses tested (n = 10; **p < 0.05 vs vehicle, main effect of dose; #p < 0.05 vs vehicle, dose × delay interaction). C, Post hoc analysis comparing 500-ng dose of LY341495 to vehicle. The 500-ng dose impaired performance across all delays in all rats compared to vehicle performance, p < 0.01. D, Micro-infusion of 500-ng LY341495 impaired performance at long delays (12–24 s) compared to vehicle performance. E, The number of trials completed did not change as a function of dose. In A, placements are mapped to standardized coronal sections corresponding to +2.70 and +3.20 mm from bregma according to the atlas of Paxinos and Watson (2005). In B, mean choice accuracy (y-axis) is plotted as a function of delay (x-axis) and dose (symbols/lines; refer to legend for specific dose). In C, D, mean choice accuracy (collapsed across all delays in C and long delays (12–24 s) in D; y-axis) is plotted as a function of the 500-ng dose of LY341495 (x-axis; symbols/lines). Error bars represent the SEM.