Figure 1.
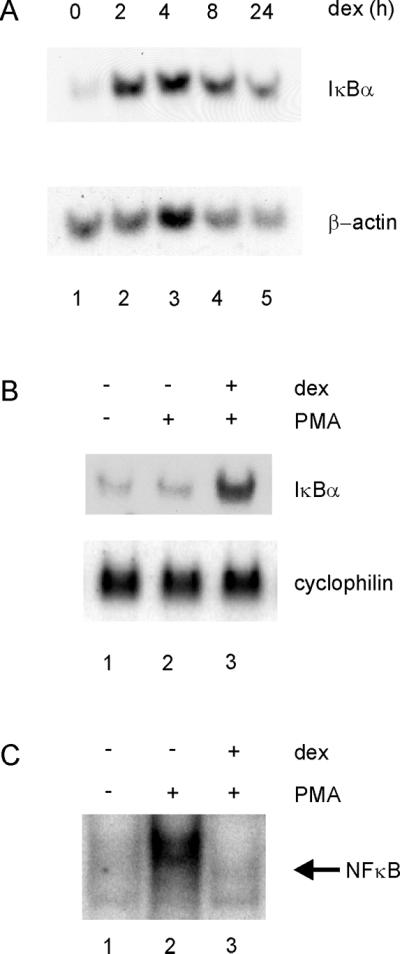
Glucocorticoids increase IκBα transcription in A1-2 cells. (A) Glucocorticoids increase IκBα RNA levels in A1-2 cells. Northern analysis was conducted with the use of A1-2 cells that were either untreated (lane 1) or treated with dexamethasone (10−7 M) for 2, 4, 8, and 24 h (lanes 2–5). Total cellular RNA was prepared and analyzed by Northern blot. Briefly, RNA was separated on a 1% agarose/formaldehyde gel, the RNA (10 μg) transferred to a nylon membrane, and the membrane probed with 32P-labeled IκBα and actin cDNA probes. (B) The NFκB activator, PMA, does not affect glucocorticoid activation of IκBα. Northern analysis was conducted with the use of A1-2 cells that were either untreated (lane 1) or treated with PMA (40 ng/ml) for 45 min (lane 2). In lane 3, cells were pretreated with dexamethasone (10−7 M) for 4 h (lane 3) before treatment with PMA (40 ng/ml) for 45 min. The blot was reprobed for cyclophilin as a control. (C) Glucocorticoids repress NFκB activity in A1-2 cells. Nuclear extracts were prepared from cells treated as in A and analyzed by gel shift, with the use of 10 μg of nuclear extract with a 32P-labeled double-stranded oligonucleotide corresponding to the NFκB consensus sequence of the IL-2 promoter. The binding reactions were analyzed on a 5% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel, followed by autoradiography.
