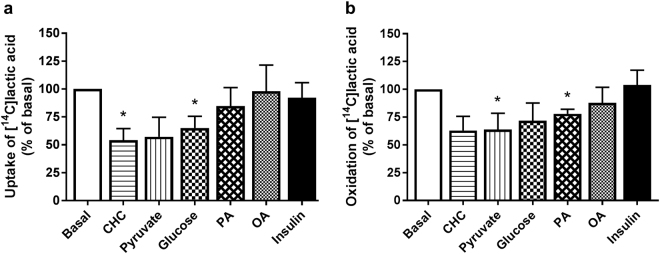
Figure 2.
Lactate metabolism in human myotubes and effects of insulin, other energy substrates and an inhibitor of monocarboxylate transporters. Lactic acid metabolism in human myotubes and the influence of acutely added insulin (100 nM), glucose (5 mM), pyruvate (5 mM), oleic acid (OA, 100 µM), palmitic acid (PA, 100 µM) or α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHC, 1 µg/ml). Myotubes were incubated with [14C(U)]lactic acid (1 µCi/ml, 100 µM) for 4 h. (a) Uptake of lactic acid was assessed as the sum of oxidized [14C]lactic acid (CO2) and remaining cell-associated radioactivity (CA) radioactivity. Basal absolute value representing 100% (mean ± SEM): 11.7 ± 5.3 nmol/mg protein. (b) Oxidized [14C]lactic acid (CO2) was trapped in a filter and counted by liquid scintillation. Basal absolute value representing 100% (mean ± SEM): 5.3 ± 2.6 nmol/mg protein. All data are presented as means ± SEM, relative to basal (n = 4–6). *Statistically significant vs. basal (p < 0.05, paired Student’s t-test).