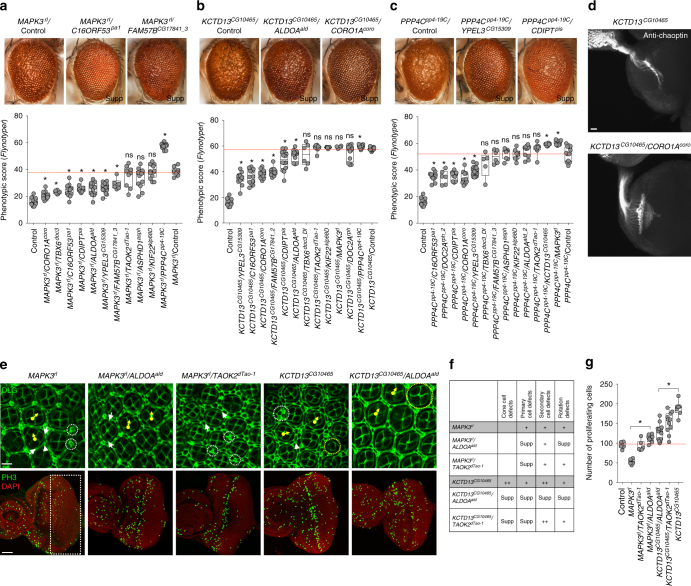
Fig. 6.
Phenotypic and functional effects of pairwise knockdown of 16p11.2 homologs. Representative brightfield adult eye images (scale bar = 50 µm) and box plots of Flynotyper scores of pairwise knockdown of a MAPK3rl with other 16p11.2 homologs (n = 6–15, *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney test), b KCTD13CG10465 with other 16p11.2 homologs (n = 4–14, *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney test) and c PPP4Cpp4-19C with other 16p11.2 homologs (n = 5–17, *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney test). d Assessment of axonal targeting in KCTD13CG10465/COROIAcoro two-hit knockdown flies. Representative confocal images of larval eye discs stained with anti-chaoptin (scale bar = 10 µm) illustrate axonal targeting from the retina to the optic lobes of the brain in eye-specific knockdown of KCTD13CG10465, and rescue of these defects with double knockdown of KCTD13CG10465 and CORO1Acoro. e Confocal images of pupal eye (scale bar = 5 µm) and larval eye discs (scale bar = 30 µm), stained with anti-Dlg and anti-pH3 respectively, for one-hit and two-hit knockdown of 16p11.2 homologs. f Table summarizing the cellular defects observed in the pupal eye of one-hit 16p11.2 flies compared to double knockdown of 16p11.2 homologs. “+” symbols indicate the severity of the observed cellular defects, while “Supp” indicates that the cellular defects were suppressed in the two-hit models. g Box plot of pH3-positive cell counts in the larval eye discs between one-hit and two-hit knockdowns of 16p11.2 homologs (n = 6-13, *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney test). All boxplots indicate median (center line), 25th and 75th percentiles (bounds of box), and minimum and maximum (whiskers)