Fig. 3.
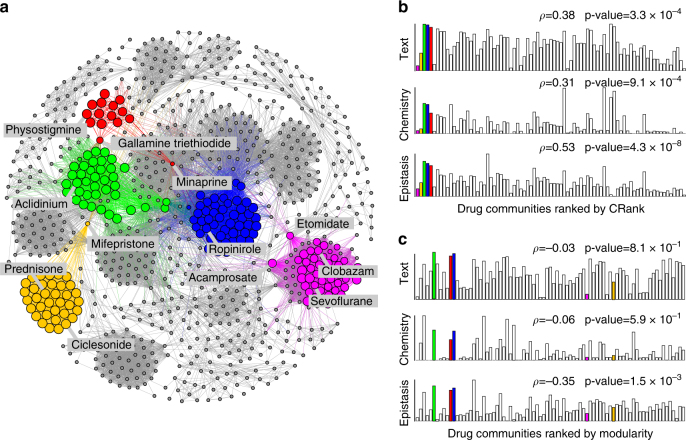
Prioritizing network communities in the network of medical drugs. a The network of medical drugs connects two drugs if they share at least one target protein. Communities were detected by a community detection method7, and then prioritized by CRank. Highlighted are five highest-ranked communities as determined by CRank. Nodes of the highlighted communities are sized by their score of the Likelihood prioritization metric (Supplementary Note 3). Investigation reveals that these communities contain drugs used to: treat asthma and allergies (e.g., prednisone, ciclesonide; yellow nodes), induce anesthesia or sedation (e.g., clobazam, etomidate, sevoflurane, acamprosate; magenta nodes), block neurotransmitters in central and peripheral nervous systems (e.g., physostigmine, minaprine, gallamine triethiodide; red nodes), block the activity of muscarinic receptors (e.g., acidinium; green nodes), and activate dopamine receptors (e.g., ropinirole; blue nodes). b, c We evaluate community prioritization against three external chemical databases (Supplementary Note 6) that were not used during community detection or prioritization. For each community we measure: (1) drug-drug interactions between the drugs (“Epistasis”), (2) chemical structure similarity of the drugs (“Chemistry”), and (3) associations between drugs derived from text data (“Text”). We expect that a true high-priority community will have more drug-drug interactions, higher similarity of chemical structure, and stronger textual associations between the drugs it contains. Taking this into consideration, the external chemical databases define three gold standard rankings of communities against which CRank is evaluated. Bars represent communities; bar height denotes similarity of drugs in a community with regard to the gold standard based on external chemical databases. In a perfect prioritization, bars would be ordered such that the heights would decrease from left to right. b CRank ranking of drug communities outperforms ranking by modularity c across all three chemical databases (as measured by Spearman’s rank correlation ρ with the gold standard ranking). CRank ranking achieves ρ = 0.38, 0.31, 0.53, while modularity obtains ρ = −0.03, −0.06, −0.35