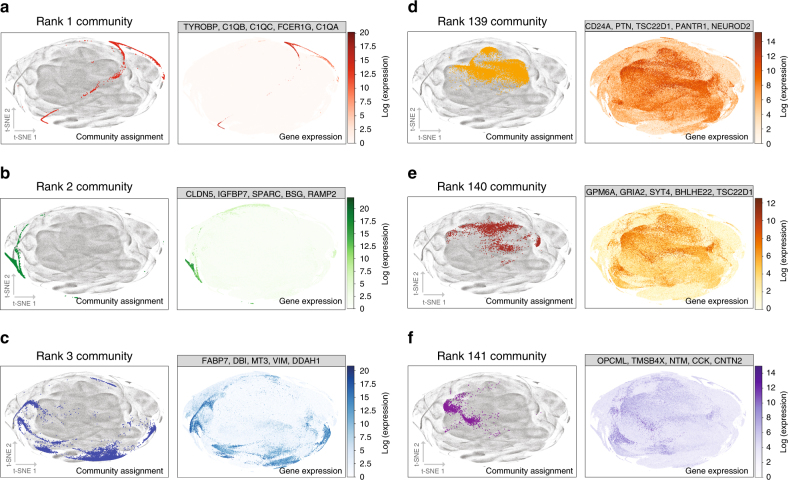
Fig. 4.
Prioritizing network communities in the megascale cell–cell similarity network. The network of embryonic mouse brain has 1,306,127 nodes representing brain cells29. Communities are detected using a community detection method developed for single-cell RNA-seq data8 and prioritized using CRank, generating a rank-ordered list of detected communities. a–c Shown are three communities that are ranked high by CRank; a rank 1, b rank 2, and c rank 3 community. t-SNE projections39 show cells assigned to each community. t-SNE is a dimensionality reduction technique that is particularly well suited for visualization of high-dimensional data. Cells assigned to each community are distinguished by color, and all other cells are shown in gray. We investigate the quality of community ranking by examining gene markers for cells in each community28. We use the single-cell RNA-seq data set to obtain a gene expression profile for each cell, indicating the activity of genes in the cell. For each community we then identify marker genes, i.e., genes with the strongest differential expression between cells assigned to the community and all other cells9. In the t-SNE projection we then color the cells by how active the marker genes are. This investigation reveals that communities ranked high by CRank are represented by clusters of cells whose marker genes have a highly localized expression. For example, marker genes for rank 1 community in a (the highest community in CRank ranking) are TYROBP, C1QB, C1QC, FCER1G, and C1QA. Expression of these genes is concentrated in cells that belong to the rank 1 community. Similarly, marker genes for rank 2 and rank 3 communities are specifically active in cell populations that match well the boundary of each community. d–f t-SNE projections show cells assigned to 3 low-ranked communities; d rank 139, e rank 140, and f rank 141 community. t-SNE projections are produced using the same differential analysis as in a–c. Although these communities correspond to clusters of cells in the t-SNE projections, their marker genes have diluted gene expression that is spread out over the entire network, indicating that CRank has correctly considered these communities to be low priority. For example, marker genes for rank 141 community in f are OPCML, TMSB4X, NYM, CCK, and CNTN2, which show a weak expression pattern that is diffused across the entire network