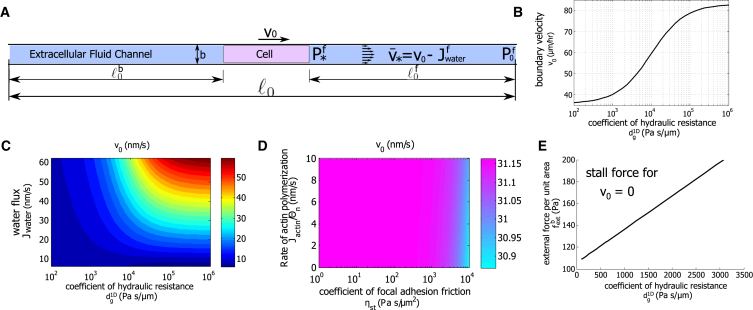
Figure 3.
Confined 1D cells migrate faster under higher coefficients of hydraulic resistance. (A) A diagram of the cell and the external fluid flow in a 1D channel is shown. (B) A model prediction of the cell boundary velocity as varies is shown. Here, mM, which corresponds to a water flux of m/h. (C) The velocity of the cell edge as and vary as shown. We let vary from 340.6 to 341 mM and obtain accordingly. Cell velocity increases with increasing and . (D) The contours of as and vary as shown. Here, Pas/μm. For confined channels with high hydraulic resistance, neither actin polymerization nor focal adhesion friction influence the cell speed significantly. (E) Stall force per unit area increases with . To see this figure in color, go online.