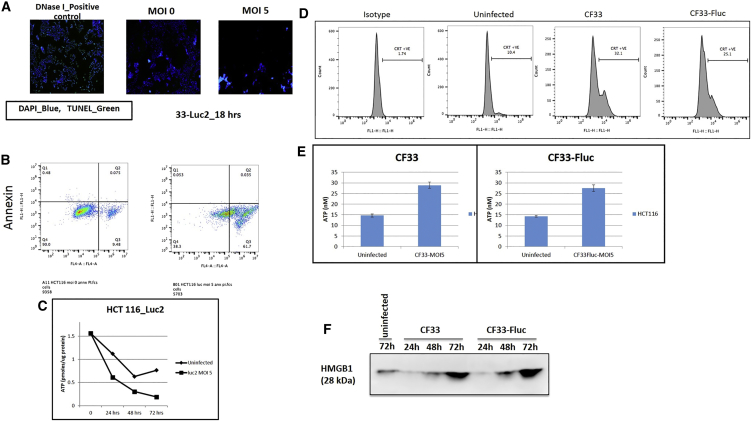
Figure 3.
Virally Induced Cell Death Occurs via Necroptotic Pathways
(A) Virally infected fluorescent microscopy shows TUNEL assay controls demonstrating fluorescent green DNA damage indicative of apoptosis, whereas both uninfected cells and highly infected cells at a high-dose MOI of 5 demonstrate no evidence of DNA damage. (B) FACS analysis of annexin and phosphatidyl inostitol (PI) examining non-infected cells (left) and infected cells (right) 18 hr post-infection. This indicates that while many dead cells are present (indicated by PI), none are undergoing apoptosis as a result of viral infection (annexin). (C) Infected cells demonstrate significantly lower quantities of ATP than non-infected controls at 48 and 72 hr. Error bars indicate SD. Student’s t test was used. *** indicates statistical significance defined as p < 001 for 48-hr and 72-hr time points. (D) Calreticulin was analyzed via flow cytometry with and without viral infection, demonstrating increased caltreticulin from infected cells. (E) ATP secretion in supernatants was demonstrated to be at least 1.5-fold higher in infected cells (error bars indicate SD). (F) HMGB1 protein secretion in supernatants of infected cells was substantially more pronounced in infected versus non-infected cells.