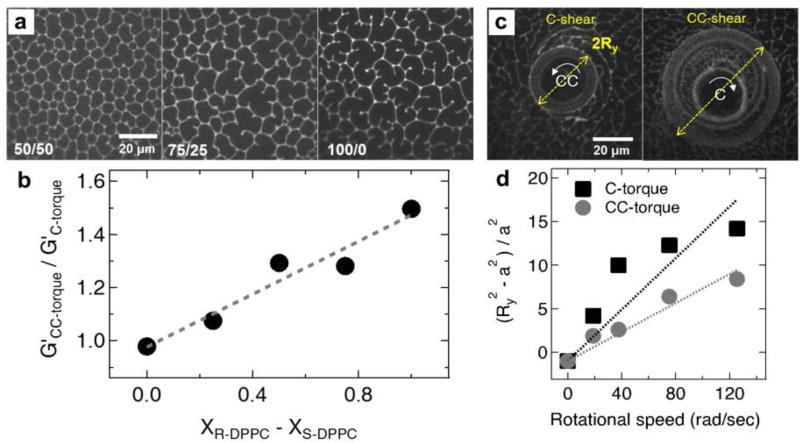
Fig. 2.
Effect of chirality on non-linear elastic modulus and yield stress. (a) Fluorescence images of 50/50 (racemic) and 75/25 r-DPPC/s-DPPC and 100% r-DPPC. As the ratio of r-DPPC to s-DPPC increases, the counterclockwise rotation of the domains increases. (b) The chiral nonlinear elasticity ratio G’c/G’cc increases linearly from 1 to 1.5 for (Xr-DPPC – Xs-DPPC) from 0.0 (racemic mixture) to 1.0 (pure r-DPPC) (c) Fluorescence images showing the area of r-DPPC monolayers yielded by microbuttons rotating at 6 Hz in the counter-clockwise (CC) and clockwise (C) directions. The yield radius Ry (arrow) is larger for monolayers with lower surface yield stresses. (d) Yield radius increases with rotation rate according to Eqn. 1, revealing the surface yield stress for C-sheared monolayers, , to be ~ 1.8 times higher than for CC-sheared , reminiscent of the nonlinear elasticity ratio.