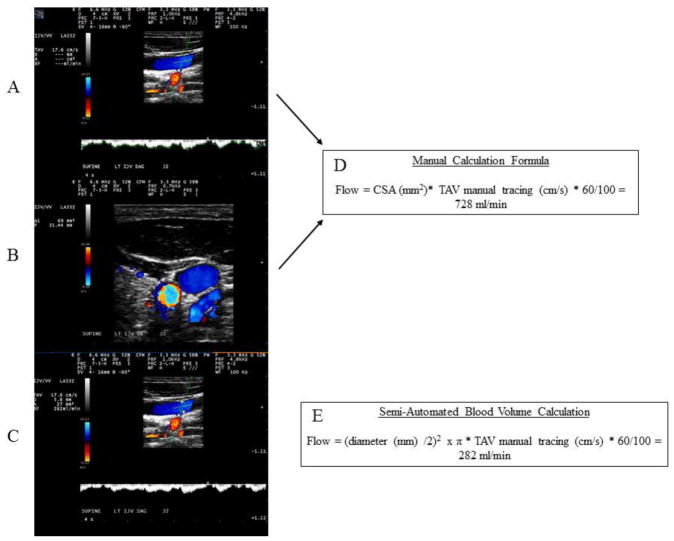
Figure 1.
Differences in the manual (top two panels) versus the semi-automated calculation of the venous blood flow volumes and the corresponding formulas.
Panels A and B demonstrate the manual method of calculation of the venous blood volume. A) Manual time averaged velocity detection. Angle of incident at or between 45° and 60° with angle correction bar parallel to vessel walls was used. B) Manual tracing of the cross-sectional area in transverse plane. Panel C depicts the semi-automated blood volume calculation with an anterior to posterior wall diameter obtained at 180° orthogonal plane alignment in regards to the vessel wall. Panel boxes D and E show the corresponding calculation formulas used to derive the internal jugular vein volume (manual versus semi-automated calculation, respectively). CSA – cross-sectional area, TAV – time average velocity, D – dimeter, ml – milliliters, min – minutes.