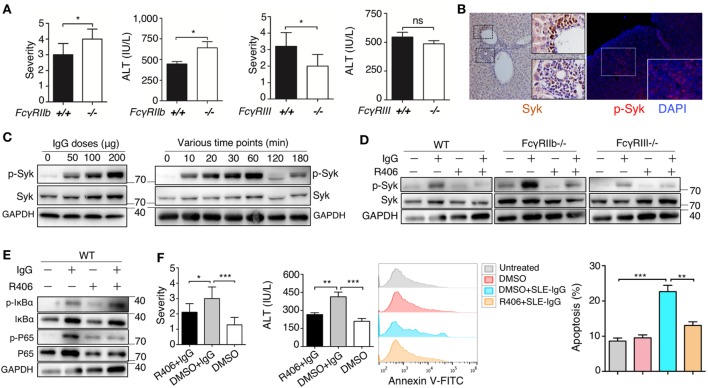
Figure 5.
Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor suppressed liver inflammation induced by deposited lupus immunoglobulin G (IgG). (A) Severity of liver inflammation and serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level 48 h after intrahepatic injection of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-IgG in mice with FcγRIIb-deficient (FcγRIIb−/−) and FcγRIII-deficient (FcγRIII−/−). *p < 0.05 (the result is representative of three independent experiments, n = 6 mice per group/experiment). (B) Representative image of Syk and p-Syk expression in inflamed liver sections from lupus-prone mice (aged 29 weeks) by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence, respectively. (C) Western Blot detected phosphorylation of Syk (p-Syk) or Syk in BMDMs stimulated by various doses of SLE-IgG for 30 min or stimulated by SLE-IgG (100 µg/ml) for the indicated time points as shown. BMDMs (2 × 106 cells) were isolated from wild-type (WT) mice. The results were from three independent experiments. (D) Western blot analyzing p-Syk or Syk in BMDMs stimulated by 100 µg/ml SLE-IgG in presence or absence of Syk inhibitor R406 (2 µM) for 30 min. BMDMs (2 × 106 cells) were isolated from WT or FcγR−/− mice. The results are from three independent experiments. (E) WT-derived BMDMs (2 × 106 cells) were stimulated with 100 µg/ml SLE-IgG in the presence or absence of Syk inhibitor R406 (2 µM) for 30 min. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis to detect the designated proteins or their phosphorylated cognates. (F) The severity of liver inflammation, serum ALT level, and analysis of apoptotic hepatocytes in C57BL/6 mice treated with or without Syk inhibitor R406 (10 mg/kg body) sacrificed 48 h after intrahepatic injection of SLE-IgG (200 µg) from a patient with lupus. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (the result is representative of three independent experiments, n = 7 mice per group/experiment).