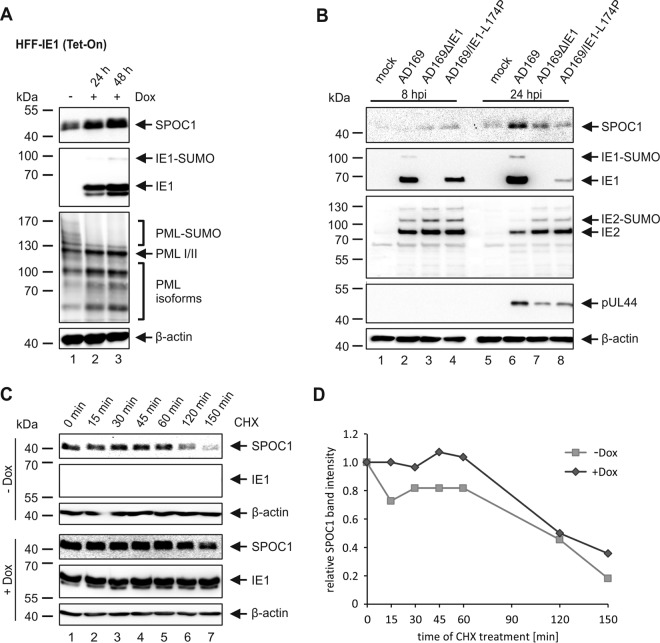
FIG 3.
The immediate early protein IE1 induces the upregulation of SPOC1. (A) SPOC1 expression levels were analyzed in doxycycline (Dox)-treated and untreated HFF-IE1 cells by Western blotting. IE1 expression was induced by treatment with 500 ng/ml doxycycline for two different time intervals (24 h or 48 h). Cells were harvested, and total cell extracts were prepared, separated by SDS-PAGE, and subjected to immunoblotting. The antibodies used were directed against SPOC1, the viral immediate early protein IE1, and the cellular protein PML (pAbs A167 and A168) as a control. (B) HFF cells were infected with wt-AD169, AD169ΔIE1, and AD169/IE1-L174P at an MOI of 2. Cells were harvested at the indicated times postinfection, and total cell extracts were prepared and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The antibodies used were directed against SPOC1, the viral immediate early proteins IE1 (mAb p63-27) and IE2 (pHM178), and the viral early protein pUL44 (mAb BS510). (C) Determination of the SPOC1 half-life in the presence and absence of IE1 using cycloheximide (CHX) in doxycycline-treated (+Dox) and untreated (−Dox) HFF-IE1 cells. Twenty-four hours after the induction of IE1 expression with doxycycline, cells were treated with 25 μg/ml of CHX and harvested at the indicated times to assess SPOC1 expression levels by Western blotting. (D) Densitometric analysis of data in panel C was performed with AIDA image analyzer v.4.22 software, and SPOC1 band intensities were normalized against their corresponding β-actin signals. For all experiments, monoclonal antibody AC-15 (β-actin) served as a loading control.