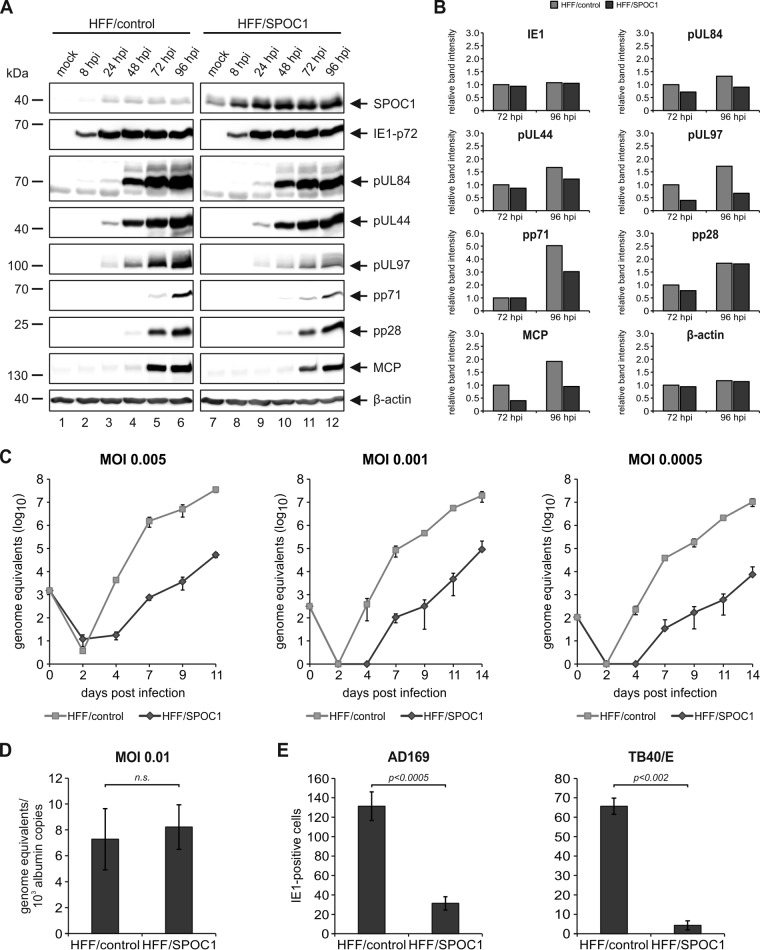
FIG 6.
SPOC1 overexpression restricts initiation of IE gene expression. (A) HFF/SPOC1 and control HFF cells were either not infected (mock) or infected with AD169 at an MOI of 1 and harvested at the indicated times for Western blotting. Expression kinetics of the viral immediate early protein IE1, viral early proteins (pUL84, pUL44, pUL97, and pp71), and viral late proteins (pp28 and MCP) were compared. (B) Densitometric analysis of the data in panel A was performed with AIDA image analyzer v.4.22 software. (C) Multistep growth curve analyses of AD169 on HFF/control and HFF/SPOC1 cells. Cells were infected with AD169, as indicated, at an MOI of 0.005, 0.001, or 0.0005, and cell supernatants were harvested at the indicated times postinfection and analyzed for genome equivalents by HCMV IE1-specific quantitative real-time PCR. (D) HFF/control and HFF/SPOC1 cells were infected with HCMV laboratory strain AD169 at an MOI of 0.01. At 8 hpi, intracellular DNA was isolated, and genome equivalents were assessed via TaqMan PCR in relation to albumin copy numbers. n.s., not significant. (E) Analysis of IE gene expression in SPOC1-overexpressing cells with AD169 and TB40/E. HFF/control and HFF/SPOC1 cells were grown on coverslips in six-well dishes, infected with 100 IEU/well of either laboratory strain AD169 or clinical isolate TB40/E, and fixed at 24 hpi. The number of IE-expressing cells was determined by indirect immunofluorescence analysis using monoclonal antibody p63-27 against the viral protein IE1. Statistical analysis was performed with Student's t test.