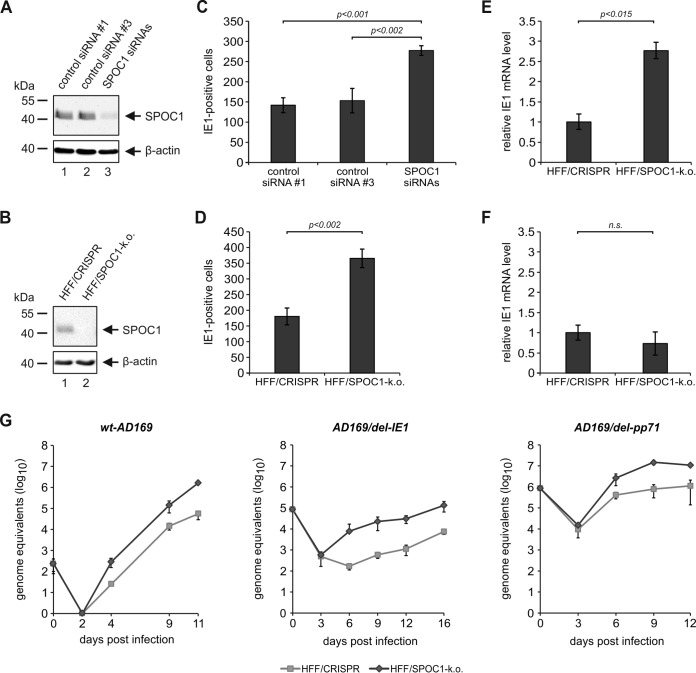
FIG 9.
More cells initiate viral IE gene expression in the absence of SPOC1. (A and B) Endogenous SPOC1 levels were diminished either by siRNA-mediated transient transfection using 100 pmol of ON-Target Plus human PHF13 (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO, USA) with two control siRNAs (siRNAs 1 and 3) (A) or by stable SPOC1 knockout using the CRISPR/Cas9 system, generated via lentiviral transduction and yielding in control (HFF/CRISPR) and SPOC1 knockout HFFs (B). Western blot analyses of endogenous SPOC1 were performed to ensure efficient SPOC1 depletion. (C and D) Analysis of IE gene expression in the absence of SPOC1 with AD169. SPOC1-depleted cells and the respective control cells were grown on coverslips in six-well dishes, infected with 100 IEU/well of either laboratory strain AD169 or clinical isolate TB40/E, and fixed at 24 hpi. The number of IE-expressing cells was determined by indirect immunofluorescence analysis using monoclonal antibody p63-27 against the viral protein IE1. Statistical analysis was performed with Student's t test. (E and F) HFF/CRISPR and HFF/SPOC1-k.o. cells were infected with HCMV laboratory strain AD169 at an MOI of 0.01 (E) or an MOI of 1 (F). At 8 hpi, total RNA was isolated with TRIzol and synthesized into cDNA via RT-PCR, and IE1 transcript levels were assessed via TaqMan PCR. The relative IE1 mRNA levels were calculated by normalization against albumin. (G) Multistep growth curve analyses were conducted in HFF/CRISPR and HFF/SPOC1-k.o. cells with wild-type AD169 (wt-AD169) or recombinant mutant viruses deprived of either IE1 (AD169/del-IE1) or pp71 (AD169/del pp71) (MOI of 0.001). Cell supernatants were harvested at the indicated times postinfection and analyzed for genome equivalents by HCMV gB-specific quantitative real-time PCR. Error bars indicate the standard deviations derived from data from three independent experiments.