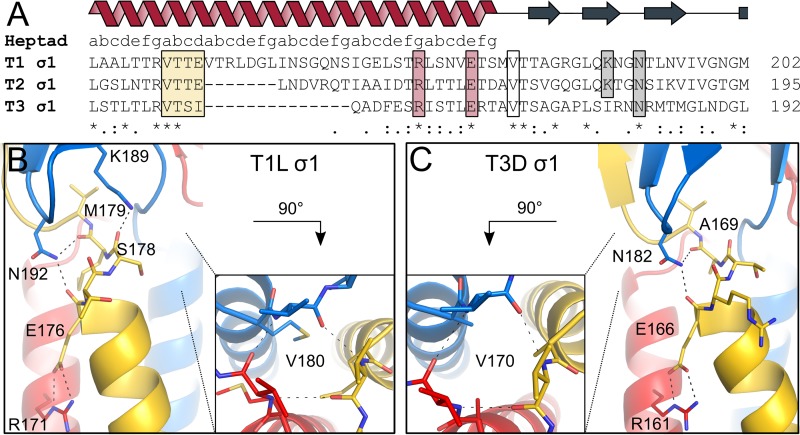
FIG 2.
Interactions between the coiled-coil and body domains. The trimeric σ1 protein is shown in blue, red, and yellow. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the site of transition between coiled-coil and body domains of the three reovirus serotypes. Conserved residues are highlighted with stars. The heptad repeat consensus sequence is indicated above the alignment. The stutter is highlighted by a yellow box. Residues involved in stabilizing the coiled-coil end and the domain transition are also outlined. (B) T1L σ1 residues N192 and K189 of the body domain, located close to the C-terminal coiled-coil end, form hydrogen bonds with the carbonyl groups of E176 and S178 and the carbonyl group of M179, respectively. An interhelical salt bridge involving R171 and E176 stabilizes the end of the coiled coil. Residue R171 also mediates contacts with S169 and S173 (not shown). Valine residues (V180) at the domain boundary form backbone-backbone interactions, shown along the trimer axis. (C) T3D σ1 residue N182 of the body domain forms hydrogen bonds with the carbonyl groups of E166 and A169, located at the C-terminal coiled-coil end. R161 forms an interhelical salt bridge with E166, stabilizing the coiled coil at the domain boundary. Residue R161 also mediates contacts with D157 and E159 (not shown). Valine residues (V170) of the three T3D σ1 subunits form backbone-backbone interactions, shown along the trimer axis.