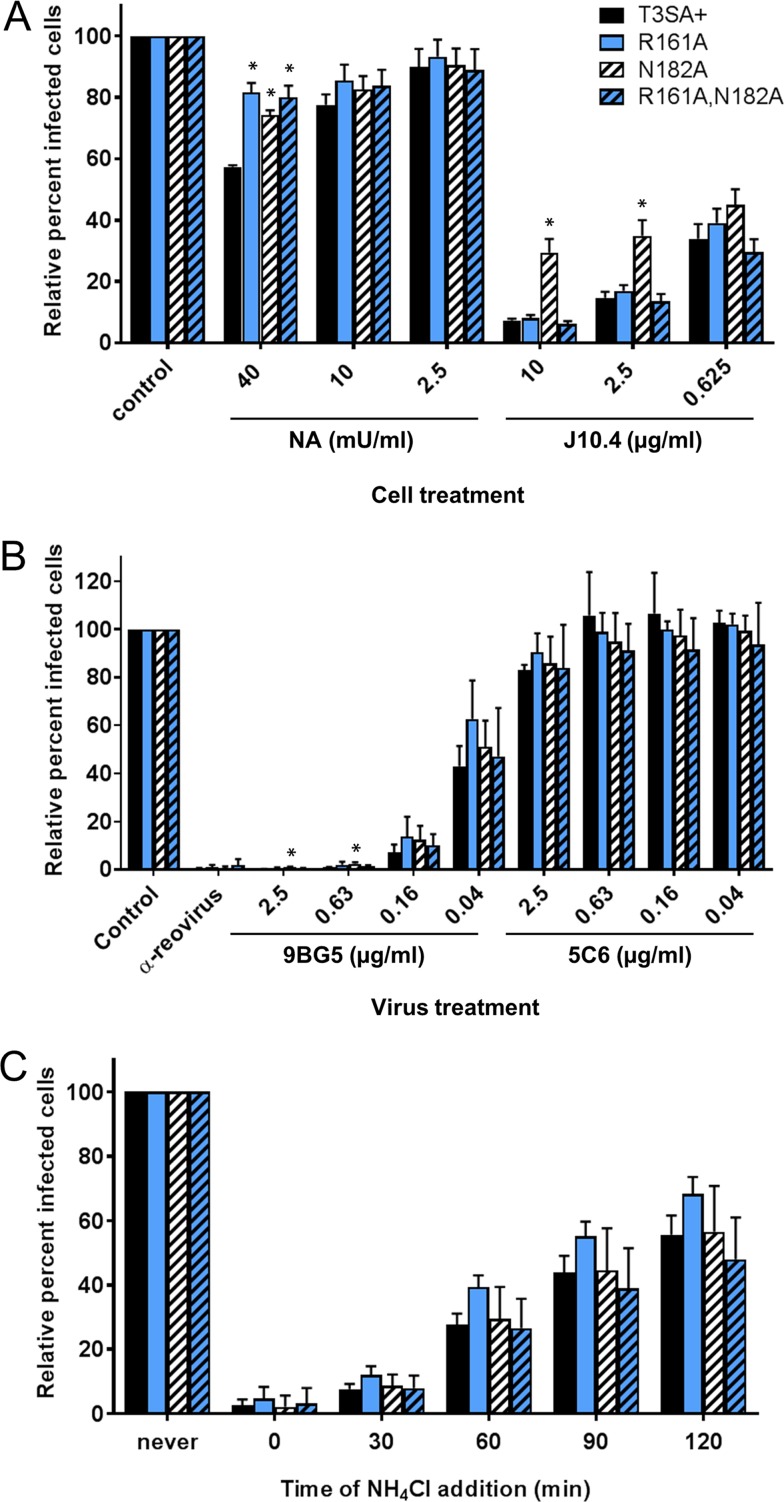
FIG 6.
Attachment and entry properties of σ1 coiled-coil-to-body transition mutant reoviruses. (A) JAM-A-CHO cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of NA to remove sialic acid or J10.4 to block binding to JAM-A or left untreated (control) prior to adsorption with equivalently infectious concentrations of rsT3SA+ or σ1 coiled-coil-to-body transition mutant reoviruses. (B) Equivalently infectious concentrations of rsT3SA+ or σ1 coiled-coil-to-body transition mutant reoviruses were incubated with polyclonal antireovirus serum as a positive control, the indicated concentrations of T3 σ1-specific MAb 9BG5 to neutralize the virus or T1 σ1-specific MAb 5C6 as a negative control, or medium only as an additional negative control prior to adsorption on L cells. (C) NH4Cl (25 mM) was added to L cells at the indicated times after adsorption with equivalently infectious concentrations of rsT3SA+ or σ1 coiled-coil-to-body transition mutant reoviruses. Cells were fixed at 16 to 20 h postadsorption and scored for DAPI and reovirus antigen by indirect immunofluorescence. Results are expressed as the mean percentages of virus-infected cells, relative to those under untreated conditions, plus standard deviations (error bars) from four fields of view per well in duplicate wells for three independent experiments. Values that differ significantly from those for rsT3SA+ under each condition by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparison test are indicated with * (P < 0.01).