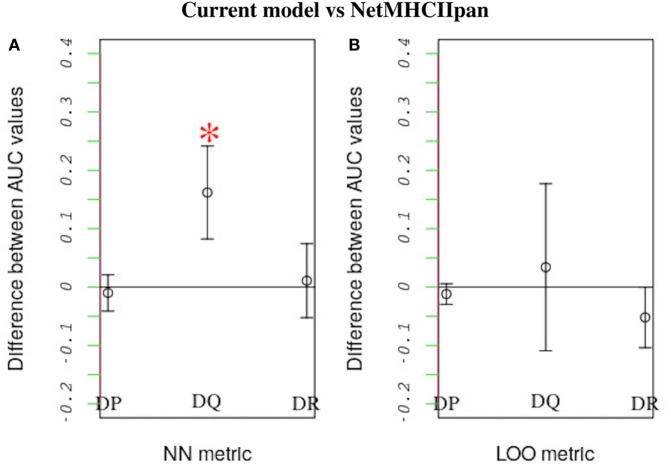
Figure 6.
Performance comparison between our model and NetMHCIIpan. Each model was used to predict the probability of peptide binding to query alleles belonging to each of three HLA loci (i.e., HLA-DP, HLA-DQ, and HLA-DR) after training it using peptide-binding data for a different allele. The allele that was most similar to the query allele was used for training. As in previous work (18), similarity between HLA alleles was defined based on two metrics: nearest neighbor (NN) and leave-one-out (LOO). See the text for definitions of these metrics. For each query allele, we measured each model’s predictive performance (accounting for both sensitivity and specificity) by calculating an AUC value. The higher the AUC value the better the predictive performance. The plot shows the average difference between the AUC values for alleles belonging to the same locus obtained using our model vs. the corresponding values obtained using NetMHCIIpan, when similarity is defined based on either (A) the NN or (B) the LOO metric. Error bars denote SDs. Strikingly, our model performs better than NetMHCIIpan when predicting peptide binding to HLA-DQ using the NN metric (p-value = 0.015). For all other cases, both models have equivalent performance.