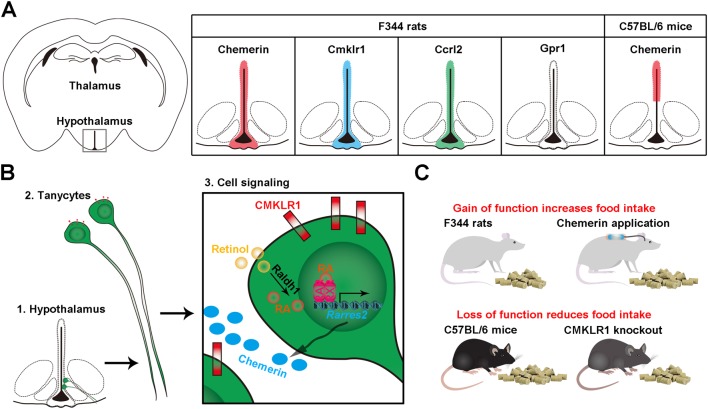
Figure 2.
The expression, signalling and function of chemerin in the hypothalamus. (A) Chemerin, Cmklr1, Ccrl2 but not Gpr1 are expressed in the tanycytes and ependymal cells lining the third ventricle of the hypothalamus of F344 rats (Helfer et al. 2016). In C57BL/6 mice, chemerin expression is restricted to ependymal cells (Miranda-Angulo et al. 2014). (B) In tanycytes, chemerin is downstream of retinoic acid signalling. Retinol enters the tanycytes where it is synthesised to retinoic acid (RA). RA enters the nucleus and binding to its receptors RAR and RXR leads to transcription of Rarres2, which is translated into chemerin. Chemerin binds to its receptor CMKLR1 and activates its downstream signalling pathway in an autocrine or paracrine manner. (C) In general, long-term application of chemerin increases food intake and loss of function reduces food intake, although contradictory results have been reported.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a