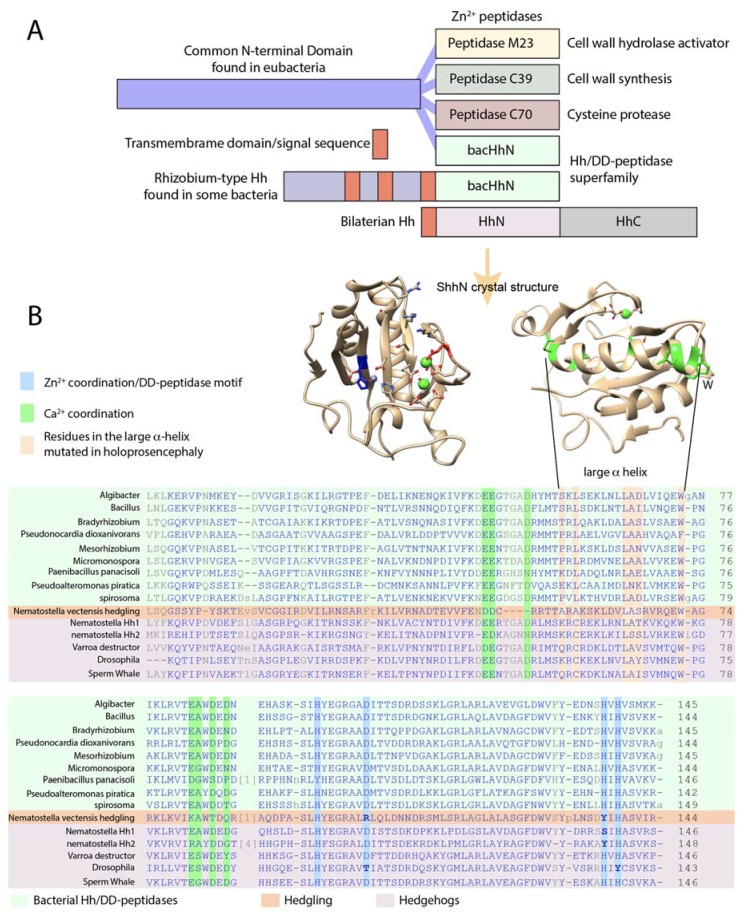
Figure 4.
The Hh/DD-peptidase family. (A) Diagram of the structure of the DD-peptidases in bacteria and animals. In bacteria, the peptidases are the C-terminal domains of larger proteins. In all cases, the peptidase domain is predicted to be located in the periplasmic space. In Rhizobium Hh, the third transmembrane domain (red) is at the same position as the signal sequence in metazoan Hh (red). (B) Lineup of the Hh/DD-peptidase domains of bacteria (green background), Hedgling (salmon background) and Hhs (purple background). Mutations in the Zn2+ coordinating/DD-peptidase motif defining residues in Hedgling and Drosophila Hh are indicated in bold. The blue columns indicate residues involved in Zn2+ coordination and define the DD-peptidase motif; the green columns indicate residues involved in Ca2+ binding. Varroa is typical for all non-Drosophilid insects. Aligned sequences are in the Supplementary file.