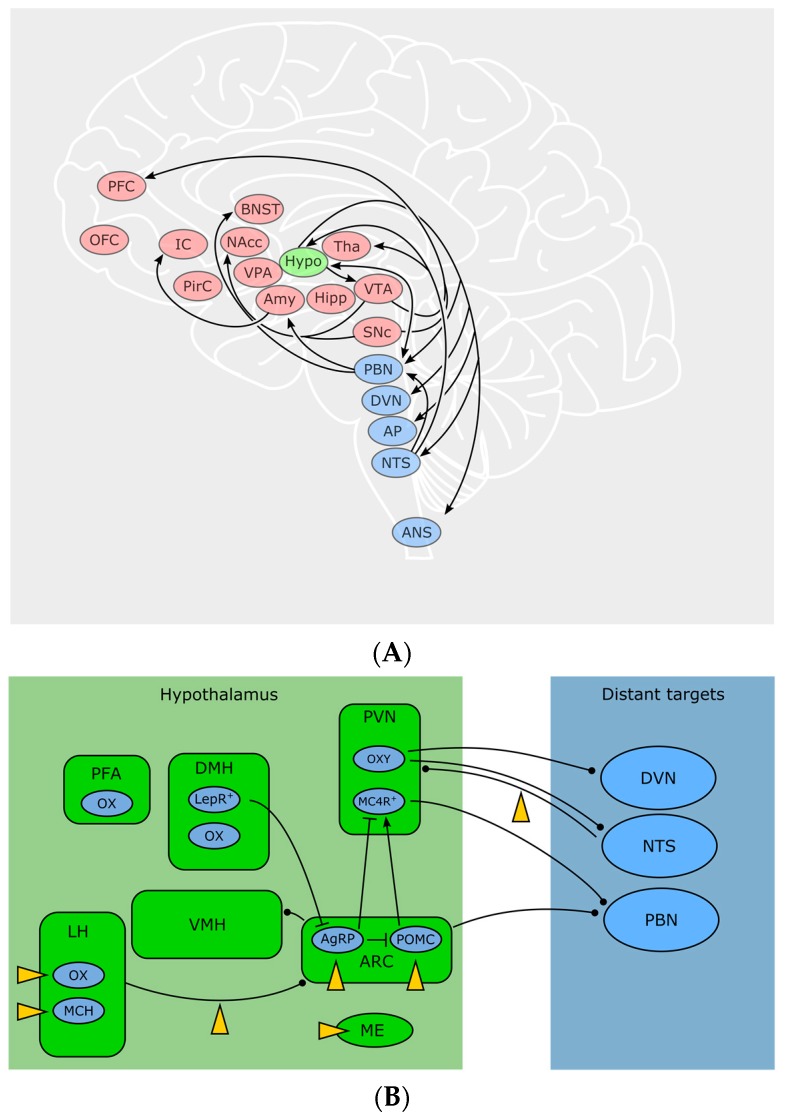
Figure 2.
(A) Brain regions where the ECS influences different aspects of feeding. Blue: autonomous “hotspots” that convey sensory and visceral information from the periphery to the CNS and vice versa. Green: the hypothalamus is of pivotal significance for the integration of humoral and neuronal signals that evaluate the calorie supply of the whole body. Red: areas especially important for motivation, decision-making, emotion and reward—influencing complex behaviors such as foraging and the choice of food. Abbreviations: PFC prefrontal cortex, OFC orbitofrontal cortex, IC insular cortex, PirC piriform cortex, BNST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, NAcc nucleus accumbens, VPA ventral pallidum, Amy amygdala, Hypo hypothalamus, Tha thalamus, Hipp hippocampus, VTA ventrotegmental area, SNc substantia nigra, pars compacta, PBN parabrachial nucleus, DVN dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve, AP area postrema, NTS Nucleus of the solitary tract, ANS autonomic nervous system. (B) Pathways and cell types of hypothalamic circuits and their distant connections with the autonomous system. endocannabinoid system (ECS) targets marked by yellow arrowheads. Abbreviations: PFA perifornical area, LH lateral hypothalamus, DMH dorsomedial hypothalamus, VMH ventromedial hypothalamus, PVN paraventricular nucleus, ARC arcuate nucleus, ME median eminence, OX orexin, MCH melanin-concentrating hormone, LEPR leptin receptor, OXY oxytocin, MCR4 melanocortin type 4 receptor, DVN dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve, NTS nucleus of the solitary tract, PBN parabrachial nucleus.