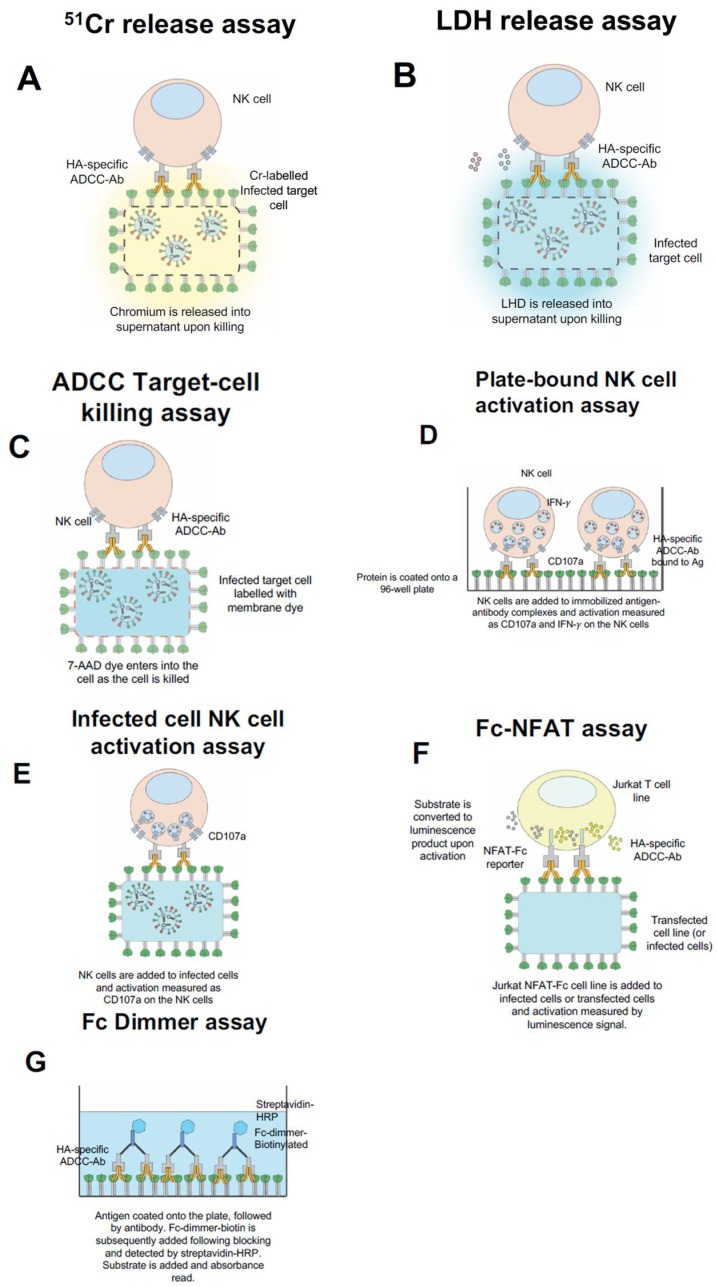
Figure 1.
Common in vitro influenza Fc-receptor assays. 51Cr-release assay, whereby infected target cells are labelled with chromium and exposed to PBMCs or purified NK cells with serum/Ig. As cells are killed the chromium is released into the supernatant (A). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay, whereby infected target cells are exposed to PBMCs or purified NK cells with serum/Ig and the release of LHD is measured in the supernatant (B). ADCC Target Killing assay, whereby the infected target cells are labelled with a membrane dye, incubated with PBMCs or purified NK cells and with serum/Ig. The killing of the infected target cell results in the uptake of 7-AAD dye and subsequently can be detected by flow cytometry (C). Plate-bound NK cell activation assay, whereby the antigen is coated onto the well of a 96-well plate, subsequently serum/Ig is added, and then PBMCs or purified NK cells are added (D). Infected-cell NK cell activation assay, wherein the infected target cells are incubated with PBMCs or purified NK cells with serum/Ig (E). For both (D,E), NK cell activation is measured by the expression of surface CD107a and intracellular IFN-γ by flow cytometry. Promega Fc-FNAT assay, wherein Jurkat NFAT-Fc cell line is incubated with infected or transfected target cells with serum/Ig and substrate is added. Following activation, the substrate is converted to a luminescence product which can be measured in the supernatant (F). Fc dimmer assay, wherein antigen is coated onto a plate, followed by the addition of serum/Ig. Then Fc-dimmer-biotin is added and detected by the addition of streptavidin-HRP followed by substrate (G).