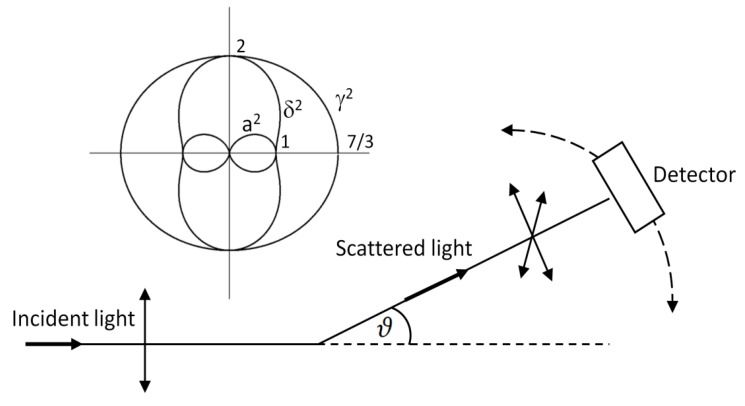
Figure 4.
Angular dependence of the Raman signal. When both the incident and scattered fields are polarized parallel to the scattering plane or when one field is polarized parallel and the latter is unpolarized, the detected Raman intensity will be angular-dependent. Angular dependences for molecules with a dominant contribution of , and respectively when moving the detector by an angle from 0° to 360° and no analyser is used are indicated in the inset.