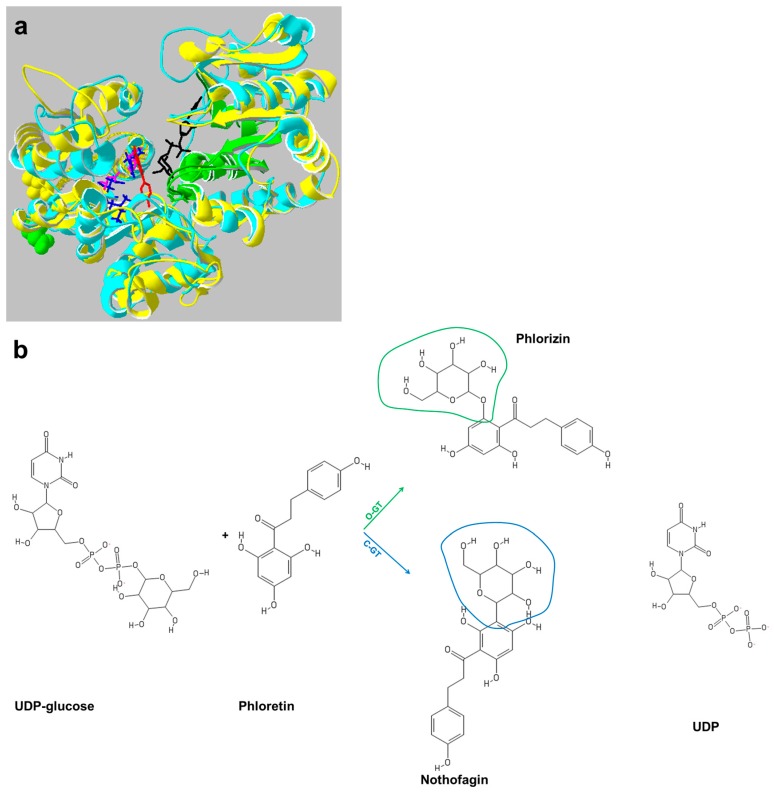
Figure 2.
X-ray crystal structure of O-GT from Vitis vinifera (VvO-GT, PDB: 2C1Z) superimposed on the homology model of C-GT from Oryza sativa (a) and the GT-catalyzed reaction (b). (a) Yellow/light green, VvO-GT; left, N-terminal domain showing catalytic H20 and D119 residues (pink); right, C-terminal domain showing the green PSPG motif that binds the donor sugar (black). Here the donor analogue is UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose; Red, acceptor (kaempferol). Turquoise/dark green, rice-CGT; left, N-terminal domain showing H24, D120 and I121 residues (blue); right, C-terminal domain showing the dark green PSPG motif that binds donor sugar (black). Please note that the two imidazole rings of H20 and H24 are at almost right-angles to each other. The homology model was created by I-TASSER [150] and structures visualized by Swiss PDB Deepview 4.1 [151]. (b) Reactions catalyzed by O-GT and C-GT. The nucleotide sugar donor (UDP-glucose) reacts with phloretin to give the respective O- or C-glycosides.