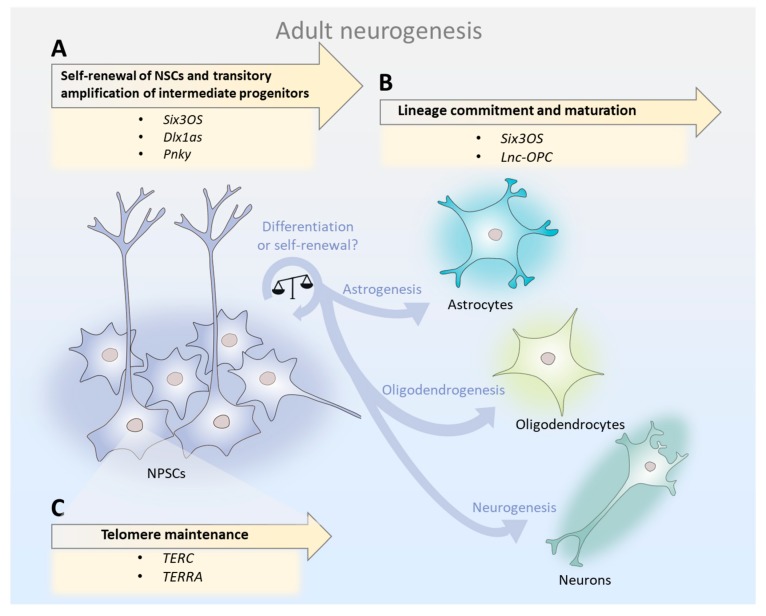
Figure 1.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) orchestrate temporally and spatially precise gene regulatory networks involved in the course of adult neurogenesis. (A) lncRNAs influence neural stem cells’ (NSCs) proliferation, expansion of transit-amplifying cells and differentiation into neuroblasts. In aging, mild alterations in lncRNA expression in the subventricular zone (SVZ) may compromise these processes, thus accounting for a decline in neurogenesis. (B) lncRNAs participate in lineage commitment and cell maturation. In the aged SVZ, the balance between lncRNAs involved in glial and neuronal fate specification may determine the cell fate of NSCs, leading to alterations in long-term neuronal/glial turnover. (C) lncRNAs are critical for telomere homeostasis. It is likely that an interplay between the telomeric lncRNAs TERRA (telomeric repeat containing RNA) and TERC (telomerase RNA component) regulates telomerase activity and the survival of NSCs during aging.