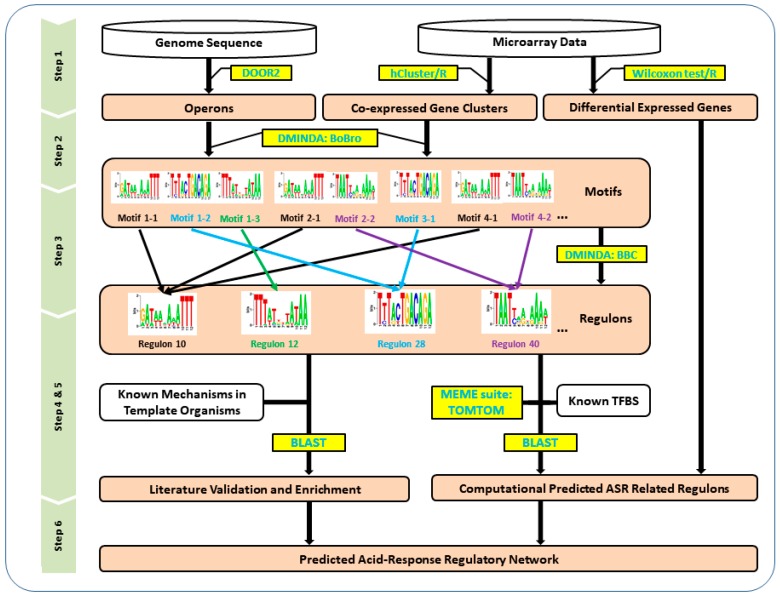
Figure 1.
The flowchart of constructing the global acid stress response (ASR) transcriptional network in MG1363. Step 1: microarray data was used to generate co-expressed gene clusters and differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and the MG1363 genome sequence was used to find operons. Step 2: a motif finding progress was carried out to identify all statistically significant motifs in each of the co-expression gene modules (CEMs). Step 3: a regulon finding procedure was designed to identify all the possible regulon candidates encoded in the genome based on motif comparison and clustering. Step 4: the motifs of each of these regulons were compared to known transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs), and differential gene expression (DGE) analysis between low pH conditions and normal conditions was used to figure out the ASR-related regulons. Step 5: regulon validation based on literature information verified the significant putative regulons and expanded the results to some insufficiently significant regulons. Step 6: the ASR-related gene regulatory network (GRN) in MG1363 was predicted and described with eight regulons, nine functional modules, and 33 genes. The combination of the above information forms a genome-scale regulatory network constructed for ASR. Abbreviations: DOOR2, Database of Prokaryotic Operons 2.0; BBC, BoBro-based motif comparison; BLAST, basic local alignment search tool; BoBro, Bottleneck Broken.