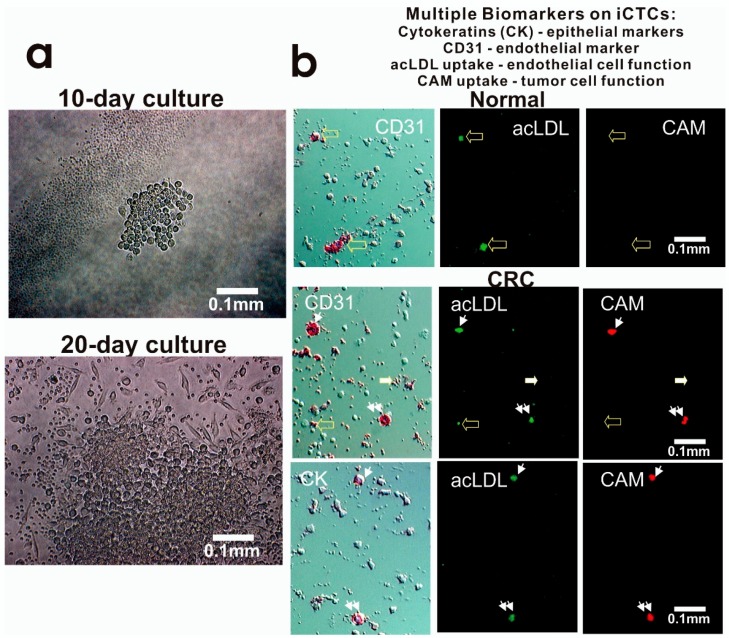
Figure 5.
Proliferative and invasive activities and expression of multiple cell lineage markers of iCTCs in blood of CRC patients. (a) Proliferation and differentiation of iCTCs into epithelial colonies ex vivo. CAM-enriched cells were cultured on the CAM scaffold for ten days and twenty days. Live cells were photographed under phase contrast microscopy. Tumor cells grew in clusters with large epithelioid cells but hematologic cells (solitary small cells and platelet-like cell fragments seen in the lower image) decreased in number and became not evident; (b) iCTCs express epithelial and endothelial biomarkers as well as display epithelial and endothelial functions. Cell multipotency of iCTCs was verified in single cells using expression of epithelial cytokeratins (CK) and endothelial CD31, acLDL uptake of endothelial function, and CAM uptake of tumor progenitor cell function. Background cells that were not labeled with antibody staining were leukocytes and platelets co-isolated with iCTCs. (Upper) panel: circulating endothelial cells in normal blood were seen to be CD31+ acLDL uptake+ but CAM uptake−. (Middle) panel: iCTCs in blood of a Stage IV CRC patient were seen to show CD31+ acLDL uptake+ CAM uptake+ (indicated by small arrows and double small arrows). However, circulating endothelial cells and platelets were seen to be CD31+ acLDL uptake± CAM uptake− (indicated by large solid and open arrows). (Lower) panel: iCTCs in blood of a Stage IV CRC patient were seen to show CK+ acLDL uptake+ CAM uptake+ (indicated by small arrows and double small arrows).