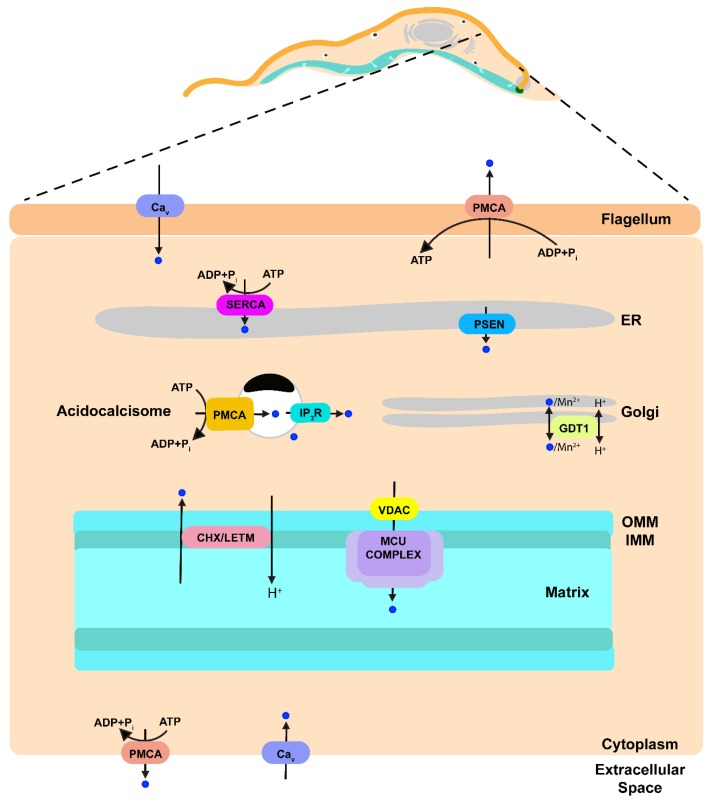
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of Ca2+ transport pathways within a model trypanosomatid parasite based on data published previously. Ca2+ is indicated as blue circles. Ca2+ upon entering the cell through a Ca2+ channel can be sequestered into the ER by the action of SERCA, into the mitochondrion by the action of MCU complex or into the acidocalcisomes by the action of a PMCA. Ca2+ release from the mitochondrion is through a Ca2+/H+ exchanger (CHX) that could be LETM1. Ca2+ from acidocalcisomes is released when IP3 stimulates the IP3R located in this organelle. A presenilin can be a leak channel in the ER. Ca2+ release through the parasite plasma membrane is achieved by a PMCA. PMCA, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase; Cav Voltage gated Ca2+ channel; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; IP3R, IP3 receptor; GDT1, GCR1 dependent translation factor; MCU complex, mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion-selective channel; Letm1 (LETM), leucine zipper-EF-hand containing transmembrane protein 1; CHX, Ca2+/H+ exchanger; PSEN presenilin; SERCA, sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane.