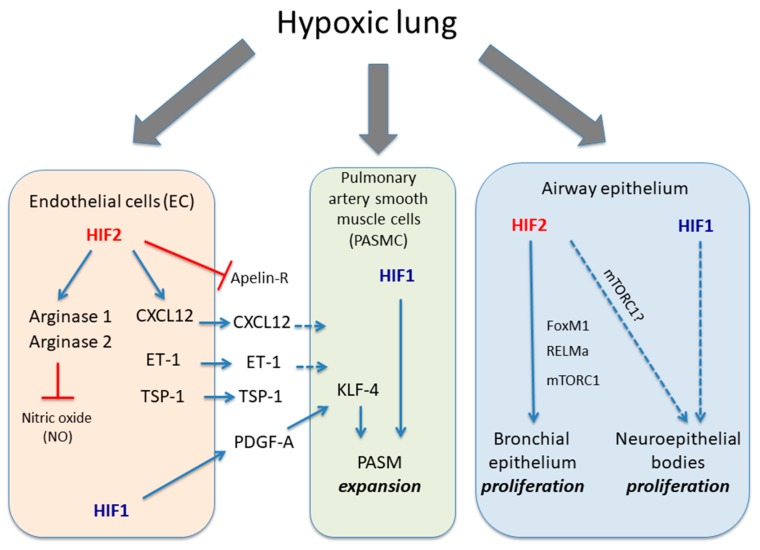
Figure 1.
Role of HIF1α and HIF2α isoforms in different lung cell types in response to hypoxia. The figure shows the biological actions executed of HIF1α and HIF2α isoforms in endothelial cells, PASMC and airway epithelium in response to hypoxia. Endothelial HIF2 induces a series of responses leading to vasoconstriction such as induction of arginase activity, which limit endothelial NO availability as well as release CXCL12, ET-1 and TSP1 in parallel with an inhibition of apelin receptor. HIF1 activity in endothelial cells can also release PDGF-B, which cooperates through KLF4 with PASMC HIF1 activity to promote their expansion. The figure also shows HIF2 activity in bronchial epithelial proliferation through potential mediators such as mTORC1, RELMα or FOXM1 as well as the potential role of HIF1α in neuroepithelial bodies proliferation located in pulmonary epithelium. Solid dark blue lines indicate activatory pathways; dashed dark blue lines indicate potential activatory actions and red lines indicate inhibitory actions.