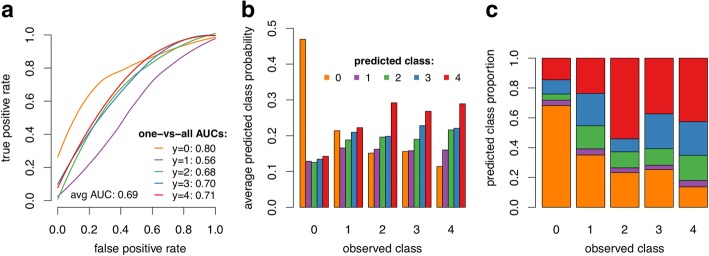
Fig. 3.
The inability of NIRS to determine sporozoite intensity. Results are for a multinomial GLM with 8 PLS components. a Average receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for one-versus-all classification models and corresponding area under the ROC curve. b The average predicted class probabilities of test observations show that uninfectious mosquitoes are easily distinguished from infectious (as there is a large difference between the largest and second-largest average predicted class probabilities). Conversely, the model has difficulty in distinguishing between the different infection groups accurately (small differences between average predicted class probabilities). c The breakdown of predicted classes of test observations gives the matrix of misclassification rates. Panel b shows the average predicted probabilities for test observations (the probability that they belong to each of the 5 classes, as given by the model). To perform classification in multinomial GLMs we choose the class for which the model gives the highest predicted probability and subsequently compute the misclassification rates (which is shown in c). The two panels give complementary information: whereas b hints at the difficulty in separating the different classes and can be used to pinpoint which classes are most confounded, c shows the actual proportions of misclassified test observation