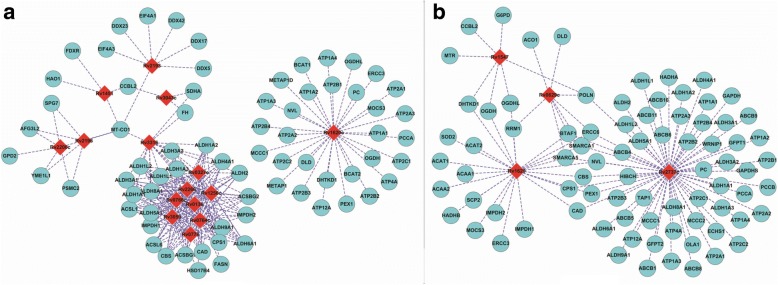
Fig. 2.
The derived interlogs between M. tuberculosis H37Rv drug-resistant genes and human genes. a illustrates the interactions of M. tuberculosis H37Rv drug-resistant genes involved in cytochromes and other target-modifying enzymes that could cause potential chemical modification of drug molecules [46]. b illustrates the interactions of M. tuberculosis H37Rv drug-resistant genes involved in SOS-response and DNA replication that lead to mutations in the gene or its regulatory region. The light blue circles denote M. tuberculosis H37Rv genes and the red diamonds denote human genes [46]