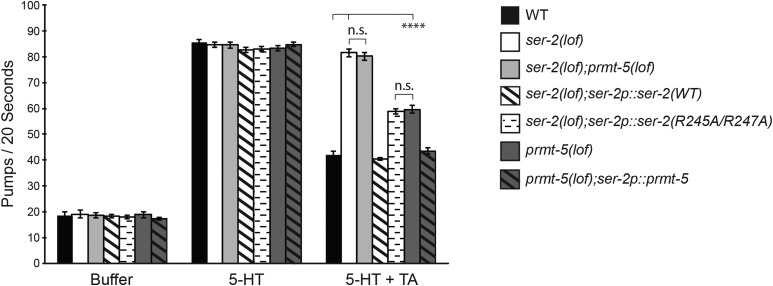
Figure 3.
C. elegans PRMT-5 promotes TA inhibition of 5-HT-stimulated pharyngeal pumping. Animals were incubated in M9 buffer, 5-HT (10 mM), or TA (2 mM) + 5-HT (10 mM). The number of pumps per 20 sec was counted. In the presence of 5-HT + TA, prmt-5(lof) animals displayed an intermediate pharyngeal pumping phenotype when compared to wild-type and ser-2(lof) animals (P ≤ 0.0001 when comparing prmt-5(lof) animals to either ser-2(lof) or wild-type animals). prmt-5(lof) animals expressing ser-2p::prmt-5 showed a pharyngeal pumping rate similar to wild-type animals (P > 0.5) in the presence of 5-HT and TA. Restoring WT SER-2 function [ser-2p::ser-2(WT)] fully rescued TA-mediated inhibition of 5-HT stimulation (P > 0.07). ser-2(lof) animals expressing SER-2(R245A/R247A) displayed a partial TA-mediated inhibition, similar to prmt-5(lof) animals (P > 0.6). The pumps per 20 sec is shown. Alleles used: prmt-5(gk357) and ser-2(pk1357). WT = the N2 wild-type strain. For rescue experiments, the combined data of three independent transgenic lines and n ≥ 42 transgenic animals are shown. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). **** P ≤ 0.0001. n.s. = not significant.